Figure 7. Cholesterol binding properties are essential for L-FABP-induced cell migration and angiogenesis.
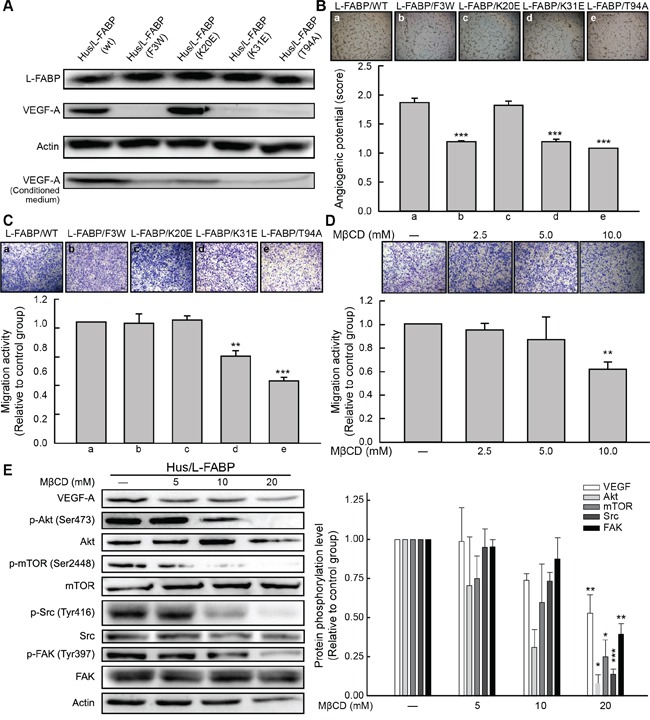
A. Western blotting analysis of L-FABP and VEGF-A expression (both intracellular and extracellular levels) in various mutants of L-FABP-overexpressed stable cells generated by site-directed mutagenesis B. In vitro angiogenic activity (score: see In vitro tube formation assay in Methods for details) of mutants. Images represent amino acid substitutions: (a) L-FABP (wild type), (b) L-FABP (F3 to W), (c) L-FABP (K20 to E), (d) L-FABP (K31 to E), and (e) L-FABP (T94 to A). ***p < 0.001 versus wild-type. C. Migration activity of the mutants. Images (a–e) represent the amino acid substitutions described in (B). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus wild-type. D. Migration activity of Hus/L-FABP cells treated with MβCD (cholesterol depletion agent: 5, 10, or 20 mM) for 12 h. **p < 0.01 versus water-treated control group. E. Western blot analysis of Hus/L-FABP cells treated with MβCD (5, 10, or 20 mM) for 6 h. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus water-treated control group.
