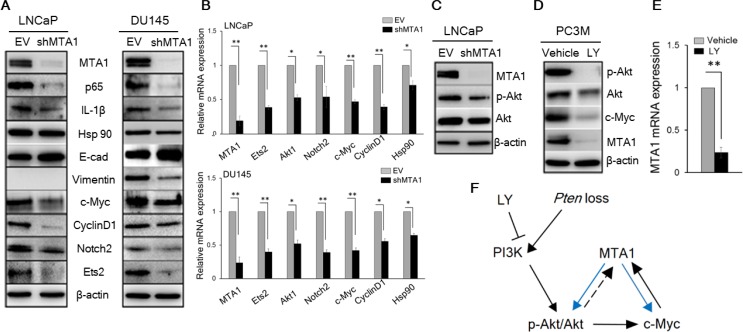
Figure 2. MTA1 directly regulates key molecular drivers of tumor promotion.
(A) Immunoblots of MTA1, NF-κB (p65), IL-1β, Hsp90, E-cadherin (E-cad), Vimentin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1, Notch2, and Ets2 in LNCaP (left) and DU145 (right) cells expressing (EV) and silenced for MTA1 (shMTA1). (B) qRT-PCR of MTA1, Ets2, Akt1, Notch2, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 and Hsp90 mRNA levels in LNCaP (top) and DU145 (bottom) EV and shMTA1 cells. (C) Immunoblot of MTA1, p-Akt and Akt in LNCaP EV and shMTA1 cells. (D) Immunoblot of p-Akt, Akt, c-Myc and MTA1 and (E) qRT-PCR of MTA1 mRNA levels in PC3M cells treated with vehicle (DMSO) and LY (LY294002). (F) Proposed mechanism involved in Pten loss-induced upregulation of MTA1, exhibiting the MTA1-Akt and MTA1-c-Myc feed-forward signaling loops (blue arrows), putative Akt-MTA1 link (dotted arrow). β-actin was used as a loading control. qRT-PCR data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (two-tailed, two-sample t-test).