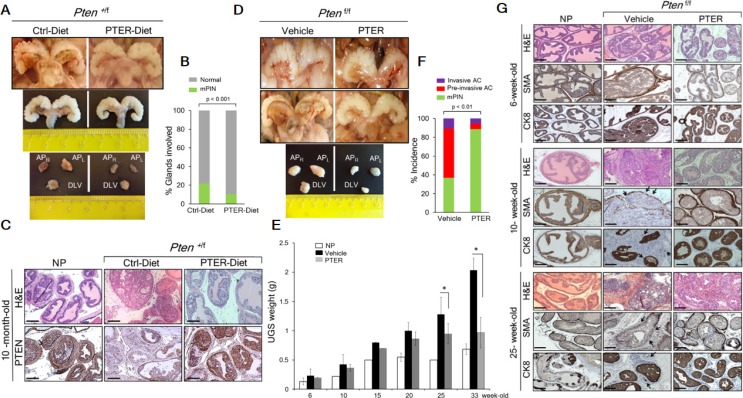
Figure 4. Pterostilbene reduces PIN formation in Pten+/f and blocks progression to adenocarcinoma in Ptenf/f mice.
(A) Gross anatomy (top) and ex vivo images (middle) of urogenital system (UGS) and dissected prostate lobes (APR, right anterior; APL, left anterior, and DLV, dorso-latero-ventral) (bottom) of the representative prostates from 10-month-old Pten+/f mice on phytoestrogen free AIN76 diet (Ctrl-Diet) and 100 mg/kg diet supplementation with pterostilbene (PTER-Diet). (B) Percentage of prostate glands from 10-month-old Pten+/f mice on Ctrl− (n = 6) and PTER-Diet (n = 7) involved in high grade mouse PIN (mPIN). p < 0.001 (Fisher's exact test). (C) Comparison of H & E prostate histology and PTEN staining in representative 10-month-old mice with NP and Pten+/f mice on Ctrl− and PTER-Diet. Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Gross anatomy of the representative UGS from 10-week-old (top) and 33-week-old (middle) Ptenf/f mice treated with vehicle (DMSO) and 10 mg/kg bw PTER. Representative images of dissected prostate lobes of Ptenf/f mice (bottom). (E) Comparison of UGS weights of vehicle or PTER treated Ptenf/f mice, isolated at the indicated ages (n = 3/group). *p < 0.05 (two-tailed, two-sample t-test). (F) Incidence of mPIN, pre-invasive and invasive adenocarcinoma (AC) in Ptenf/f mice treated with vehicle (n = 19) and PTER (n = 18). p < 0.01 (Fisher's exact test). (G) Comparison of H & E, smooth muscle actin (SMA) and cytokeratin 8 (CK8) staining from representative 6-, 10- and 25-week-old mice with NP and vehicle or PTER treated Ptenf/f mice. Arrows indicate loss of SMA staining and CK8 positive luminal cells in the stroma of vehicle treated Ptenf/f mice as signs of invasiveness. Scale bars, 100 μm.