Figure 1. PARP6 inhibits cell growth and colony formation.
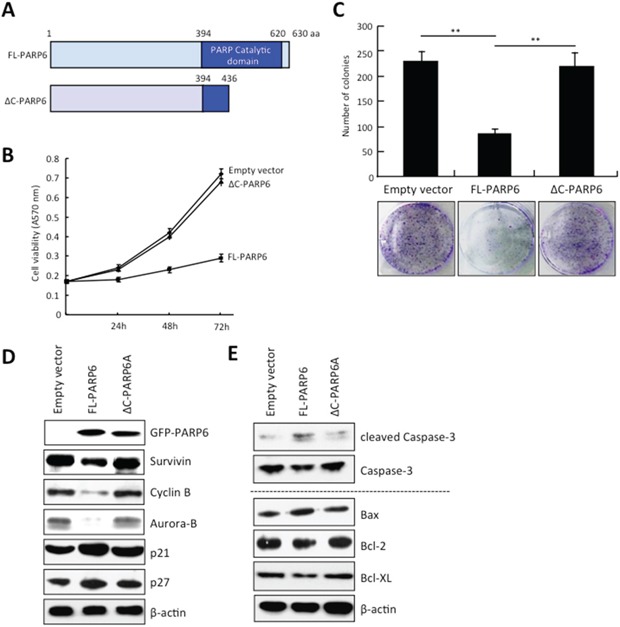
A. A schematic illustration of the human PARP6 protein. PARP6 consists of 630 amino acid residues and has a PARP catalytic domain in C-terminal region. ΔC-PARP6 lacks the PARP catalytic domain. B. Cell proliferation after FL-PARP6 and ΔC-PARP6 overexpression in SW480 cells was measured by MTT assays. After transfection with the p-EGFP-empty, p-EGFP-FL-PARP6 or p-EGFP-ΔC-PARP6 plasmids, transfectant cells (1500 cells / well) were replated in 96-well plates. The MTT assay was performed to test the cell viability at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. Values indicate mean ± SD (n=6). C. Colony formation aof FL-PARP6 and ΔC-PARP6 transfectant SW480 cells. Cells were plated in 6 cm dishes at a density of 500 cells per dish. After 2 weeks, number of colonies were counted. The data represent the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments **P < 0.01. D. Expression of cell cycle related proteins including Survivin, Cyclin B, Aurora-B, p21 and p27 in empty vector, FL-PARP6 and ΔC-PARP6 transfectant SW480 cells was examined by Western blot analysis. β-actin expression was used as a loading control. E. Expression of apoptosis related proteins including cleaved Caspase-3, Caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in empty vector, FL-PARP6 and ΔC-PARP6 transfectant SW480 cells was examined by Western blot analysis. β-actin expression was used as a loading control.
