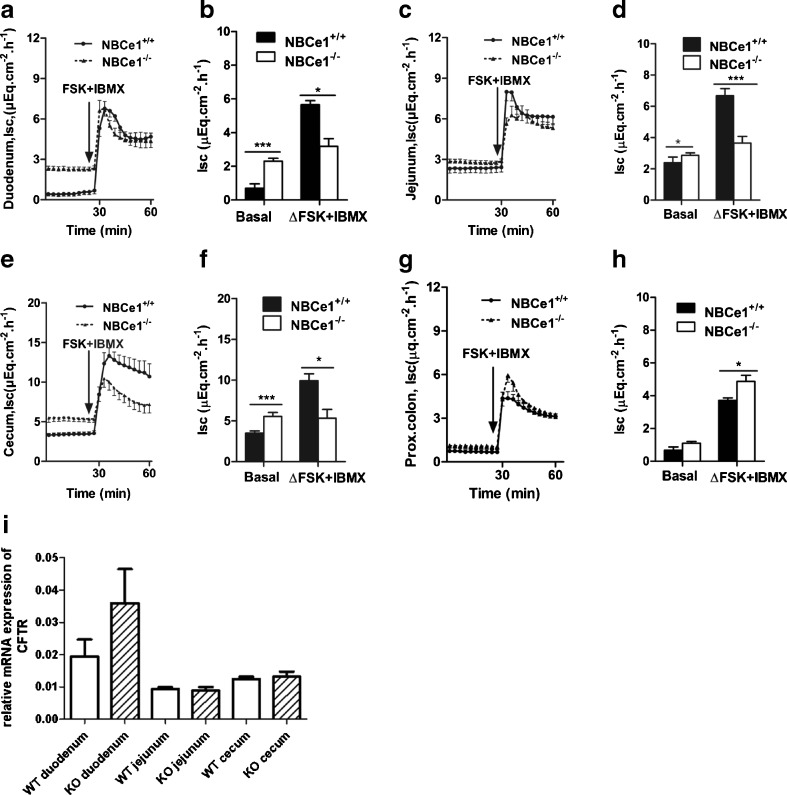
Fig. 5.
Effect of NBCe1 ablation on short-circuit current and I sc. a–f In the small intestine and cecum, but not the proximal colon, basal I sc is significantly higher in NBCe1 KO compared to WT mucosa, while the FSK-induced I sc response is significantly reduced in jejunal and cecal mucosa (see also Table 2 for PD and R t values), but higher in the proximal colon (g–h). Since an equivalent effect was not found for the J HCO3 − (see Fig. 3), the data indicate an impairment of electrogenic Cl− secretion in the absence of NBCe1 expression in the jejunal and cecal mucosa. CFTR mRNA expression, calculated in relation to the geometrical mean of the expression of villin, actin, RPS9, and cytokeratin 18, was not significantly different between NBCe1 WT and KO intestinal mucosa of the indicated segments. *P < 0.05, duodenum (n = 7), jejunum (n = 8), cecum (n = 6), and proximal colon (n = 7)