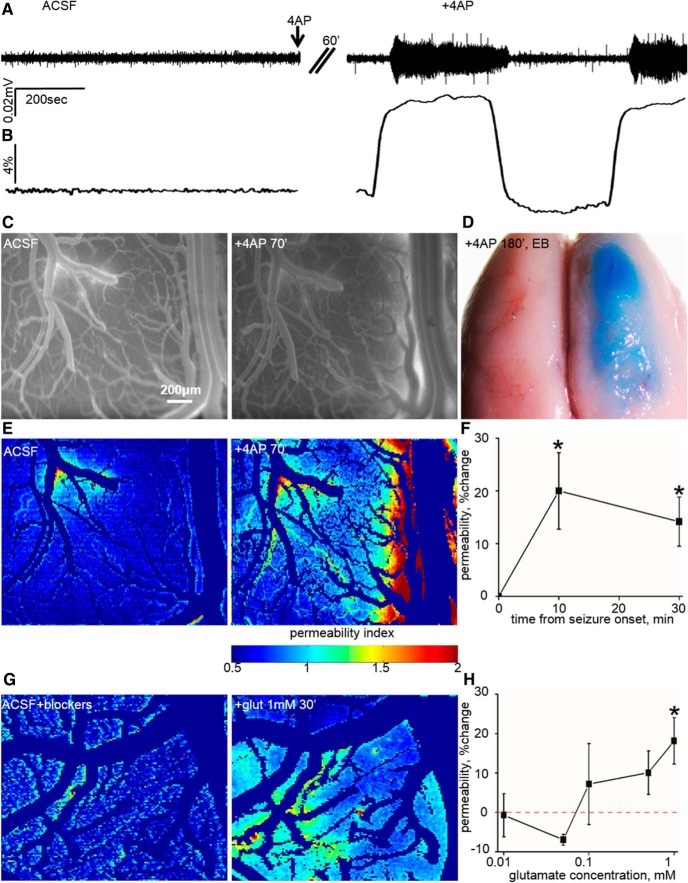
Figure 2.
BBB dysfunction after focal cortical seizures and excess glutamate. A, ECoG recordings from an anesthetized rat before (ACSF) and after topical 4-AP application (+4AP). After 60 min under 4-AP exposure, recurrent seizures were recorded. B, Seizure activity was accompanied by an increase in vessel diameter (10.05 ± 1.01%, n = 8, p = 0.01). C, Fluorescence imaging before (ACSF) and 70 min after 4-AP (+4AP 70′) showing extravascular dye, indicative of BBB dysfunction. D, The effect of recurrent seizures on the permeability of vessels is noticed by EB (see Materials and Methods) extravasation in the treated hemisphere alone. E, BBB permeability maps (color codes for the extent of permeability) depicting the effect of recurrent seizures. F, Averaged change in BBB permeability during seizures. G, Permeability maps in response to the application of glutamate for 30 min (+glut 1 mm, 30′). H, Dose response showing a gradual change in the permeability of vessels attributable to increased concentrations of glutamate (1 mm, p = 0.02, n = 9). *p < 0.05.