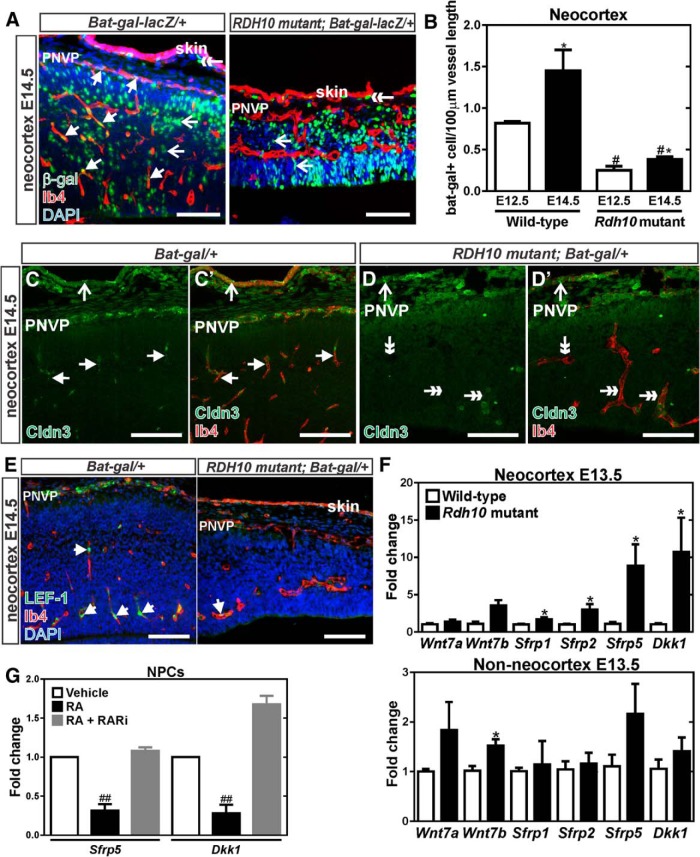
Figure 3.
Diminished WNT signaling in Rdh10 mutant cerebrovasculature. A, β-gal (green) and Ib4 (red) coimmunolabeling in neocortical blood vessels at E14.5 of Bat-gal-LacZ/+ and Rdh10 mutant Bat-gal-LacZ/+ animals. Arrows indicate β-gal+ ECs, open arrows indicate β-gal+ neural cells, and double-head arrows point to β-gal+ cells in the skin. B, Quantification of number of β-gal+ ECs per vessel length in in the neocortex of control (wild-type and Rdh10 heterozygous) and Rdh10 mutant animals at E12.5 and E14.5. *Significance between control at E12.5 and E14.5; #significance from E12.5 wild-type; *#significance from E14.5 wild-type. C, D, Arrows indicate Ib4+ (red) vessels with Claudin-3 (green) signal in the neocortical region of a control, Bat-gal/+ brain. Open arrows in the control and mutant samples indicate Claudin-3 signal in the skin overlying the brain. Double arrows indicate Claudin-3-/Ib4+ vessels in the Rdh10 mutants. E, Arrows indicate LEF-1+ (green) ECs (Ib4 in red) in the neocortex of Bat-gal-LacZ/+ and Rdh10 mutant Bat-gal-LacZ/+ animals. F, qPCR for transcript expression of WNT ligands (Wnt7a, Wnt7b) and WNT inhibitors (Sfrp1, Sfrp2, Sfrp5, and Dkk1) in wild-type and Rdh10 mutant E13.5 neocortices and non-neocortical brain structures. *Significance between control and Rdh10 mutants. G, qPCR for transcription expression of the WNT inhibitors Sfrp5 and Dkk1 in cultured neocortical progenitors treated with RA or a pan RAR inhibitor; #significance from vehicle. Scale bars, 100 μm.