Figure 9.
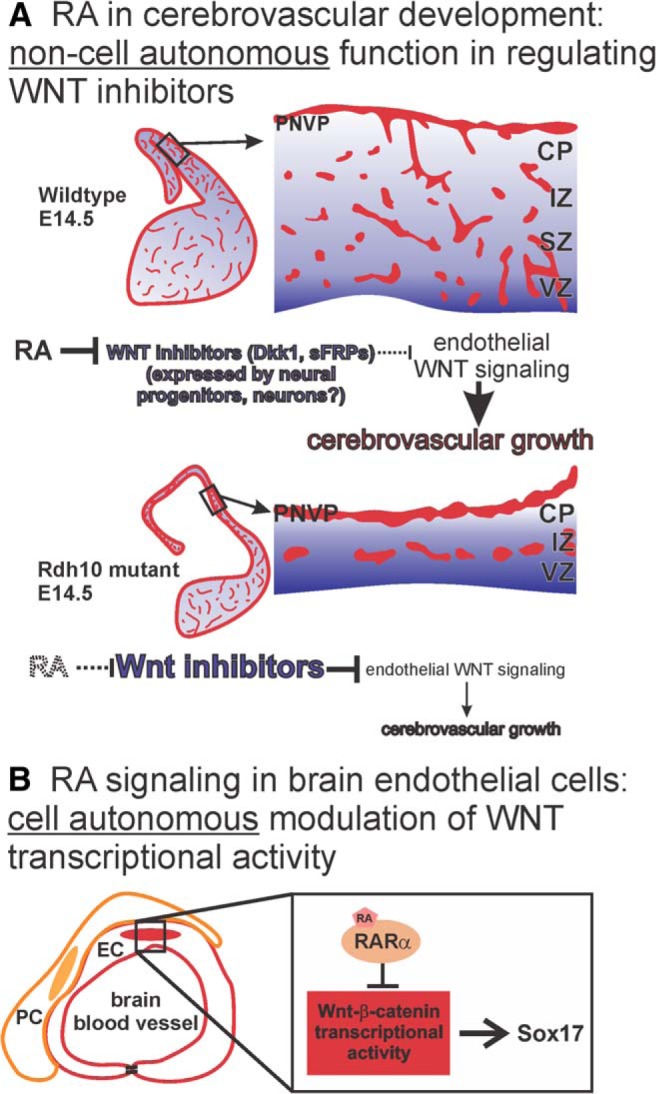
Model of RA functions during brain vascular development. A, RA in the developing neocortex normally functions to suppress expression of WNT inhibitors (Dkk1, sFRPs) to create a permissive environment for endothelial WNT signaling that drives cerebrovascular development. In RA-deficient Rdh10 mutants, ectopic expression of WNT inhibitors impedes endothelial WNT signaling, which disrupts growth of the cerebrovasculature. B, RA functions cell-autonomously in brain ECs, likely through its receptor RARα, to inhibit WNT-β-catenin transcriptional and limit expression of its target gene Sox17.
