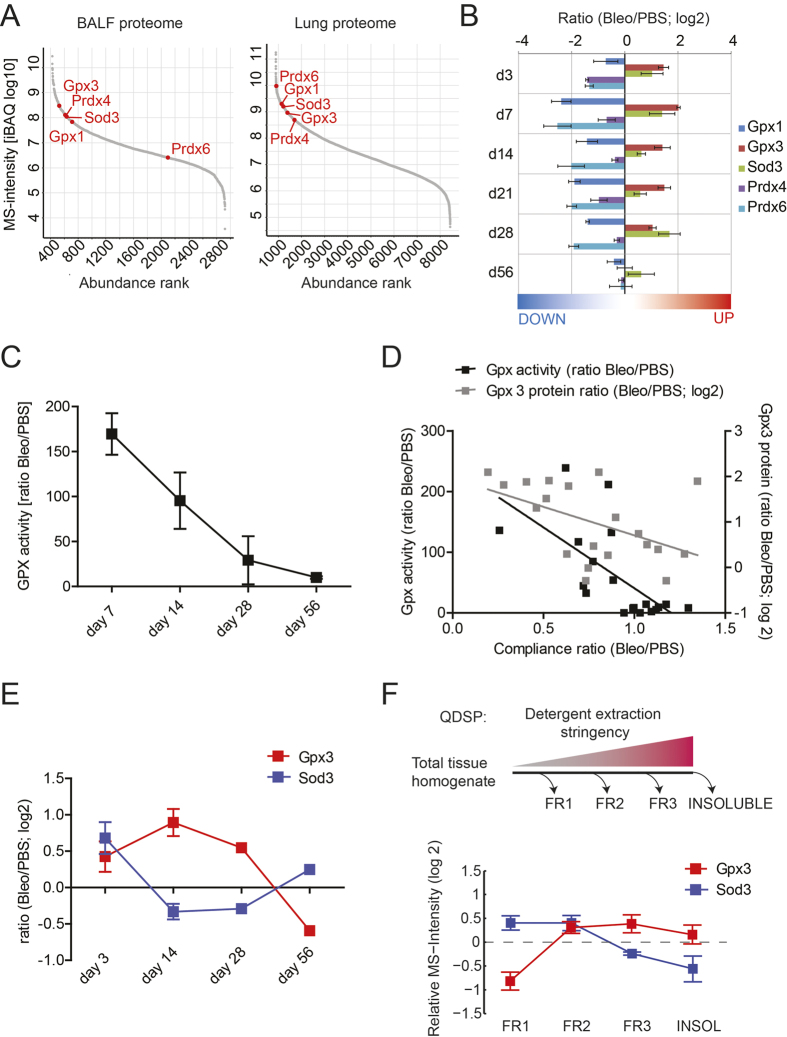
Figure 1. Of all antioxidant proteins known to associate with the extracellular compartment, only Gpx3 is upregulated both in BALF and tissue during bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis and enriched in the matrisome fraction.
(A) Label-free proteome quantification by iBAQ shows relative abundance of the proteins in BALF (left-hand panel) and the lung proteome (right-hand panel) under basal conditions, i.e. in control mice. (B) Bar graph showing regulation of major lung antioxidant proteins during bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. (C) Change of selenium-dependent Gpx activity in BALF during bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Activity ratios (i.e. Gpx activity in the Bleomycin group relative to PBS control) are shown for each time point. (D) Correlation of normalized compliance values with normalized Gpx3 protein levels as extracted from Schiller et al.35 (grey boxes) and with Gpx activity (black boxes, data from C) in the time course of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Here, data from all time points were used and correlated. (E) Regulation of Gpx3 and Sod3 in tissue during bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. (F) Quantitative Detergent Solubility Profiling (QDSP) shows enrichment of Gpx3, but not Sod3, in the insoluble fractions. The depicted data is derived from the bleomycin group at day 1435. Data in A, B, E and F were extracted from a recently acquired proteomic data set by Schiller et al.35.