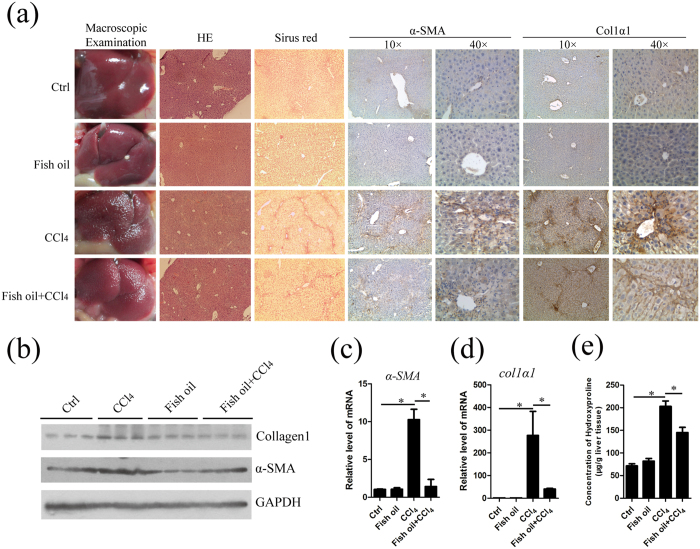
Figure 1. Fish oil attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in vivo.
Mice were treated with normal diet (control), fish oil diet (fish oil), injected with CCl4 (CCl4) or injected with CCl4 combined with fish oil diet treatment (fish oil/CCl4) on postnatal week 8. Liver tissues were used for analysis. (a) The liver histology was examined by means of macroscopic morphology, HE staining and sirius red staining. α-SMA and collagen1 signals were visualized by immunohistochemistry. (b) α-SMA and collagen1 signals were examined and quantified by western blot. GAPDH served as the loading control. The gels were cropped and the full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5. (c,d) Total RNA from liver tissue in control, fish oil, CCl4 and fish oil/CCl4 mice was isolated and subsequently used for the detection of the mRNA of α-SMA (c) and collagen1α1 (d) by real-time PCR analysis. (e) The content of hydroxyproline was detected by commercially available hydroxyproline detection kits. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM for triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05.