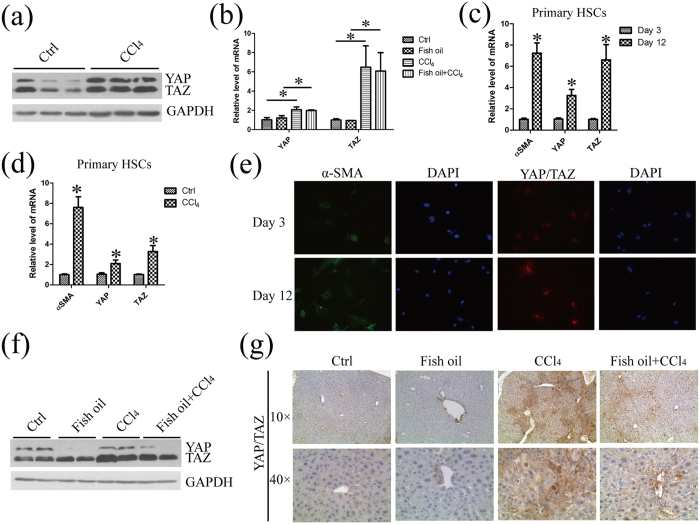
Figure 5. YAP/TAZ are over-expressed in fibrotic liver and fish oil decreases the protein level of YAP/TAZ without changing their mRNA level in liver tissue.
(a) Total protein of liver tissue in control mice and CCl4-treated mice were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis with the specified antibodies to YAP/TAZ. GAPDH served as the loading control. The gels were cropped and the full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5. (b) Total RNA of liver tissue prepared from mice of the indicated groups was used for the detection of Yap/Taz mRNA by real-time PCR analysis. (c) The total RNA was extracted from primary freshly isolated quiescent HSCs at day 3 and in vitro activated HSCs at day 12 and was subsequently used for the detection of α-SMA and Yap/Taz mRNA by real-time PCR analysis. (d) The total RNA extracted from primary freshly isolated quiescent HSCs at day 3 from healthy and fibrosis mice was applied for detection of α-SMA and Yap/Taz mRNA by real-time PCR. (e) Primary freshly isolated quiescent HSCs at day 3 and in vitro activated HSCs at day 12 were stained with antibodies against the α-SMA and YAP/TAZ by immunofluorescence. The DAPI staining (blue) was used to verify cell nucleus. (f) YAP/TAZ signaling in the liver tissue of indicated mice were examined and quantified by western blot. GAPDH served as the loading control. The gels were cropped and the full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5. (g) Liver sections from mice of the indicated genotypes were immunostained and quantified with anti-YAP/TAZ antibody. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM for triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05.