Fig 1.
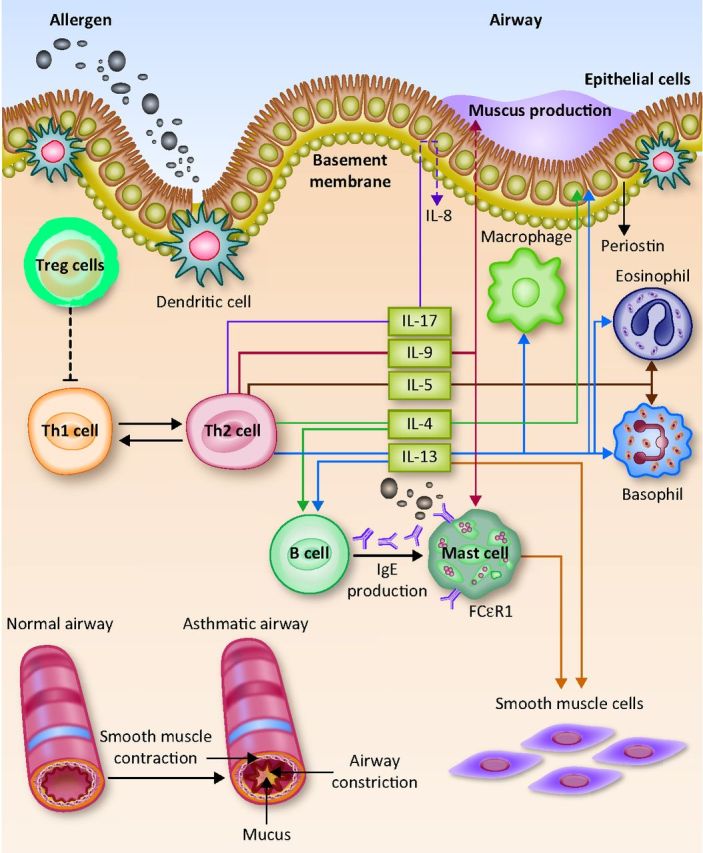
Inflammatory pathways of interleukins currently involved in asthma clinical trials. Inhaled allergens (such as pollen, dust mites and animal dander) can activate mast cells and basophils. This can trigger an acute inflammatory response in sensitive individuals, resulting in airway inflammation and airways hyper-responsiveness. Allergens are recognised and processed by dendritic cells, which drive T helper (Th) 2 differentiation and secretion of multiple cytokines, including interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 and IL-17. IL-4 and IL-13 induce B cells to produce immunoglobulin E (IgE), IL-13 induces epithelial cells to secrete periostin (a biomarker of airway eosinophilia) and IL-5 promotes the proliferation, differentiation, recruitment and survival of eosinophils. FcϵR = Fc receptors for immunoglobulin E; IG = immunoglobulin; IL = interleukin; Treg cell = regulatory T cell. Reproduced with permission from Gibeon and Menzies-Gow (2012).18
