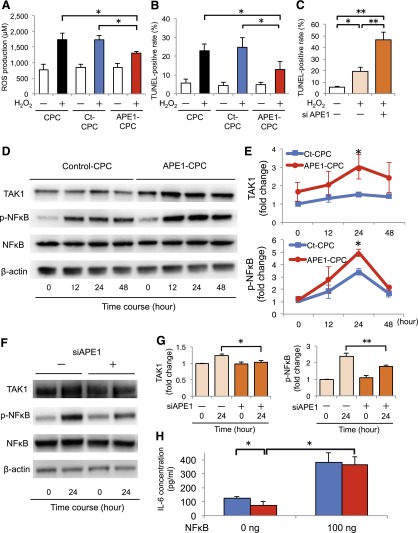
Figure 2.
H2O2-induced ROS production and apoptosis in CPCs via activation of TAK1/NF-κB signaling. (A): Graph of dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate concentration (ROS production) after H2O2 treatment for 3 hours (n = 4 per group). (B): Number of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells after H2O2 treatment for 48 hours (n = 6 per group). (C): Percentage of apoptotic CPCs transfected with siRNA against APE1 gene after H2O2 treatment overnight (n = 5, per group). (D): Representative blots of TAK1 and NF-κB expression in APE1-CPCs and control-CPCs upon TNF-α stimulation. (E): Fold change of TAK1 activation (top) and NF-κB phosphorylation (p-NF-κB; bottom) against baseline of control-CPCs (n = 7 per group). (F): Representative blots of TAK1 and NF-κB expression in CPCs with or without APE1 knockdown (siAPE1). (G): Fold change in TAK1 activation (left) and p-NF-κB (right) in APE1-CPCs relative to control-CPCs; after 24 hours of stimulation with TNF-α (n = 10 and 7 per group for TAK1 and p-NF-κB, respectively). (H): NF-κB/IL-6 ELISA assay (n = 5, respectively). Blue bar, control-CPC; red bar, APE1-CPC. ∗, p < .05, ∗∗, p < .01. Abbreviations: APE1, apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease/redox factor 1; CPC, cardiac progenitor cell; Ct, control; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; IL, interleukin; NF, nuclear factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; siRNA, short interfering RNA; TAK1, transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling.