Figure 1.
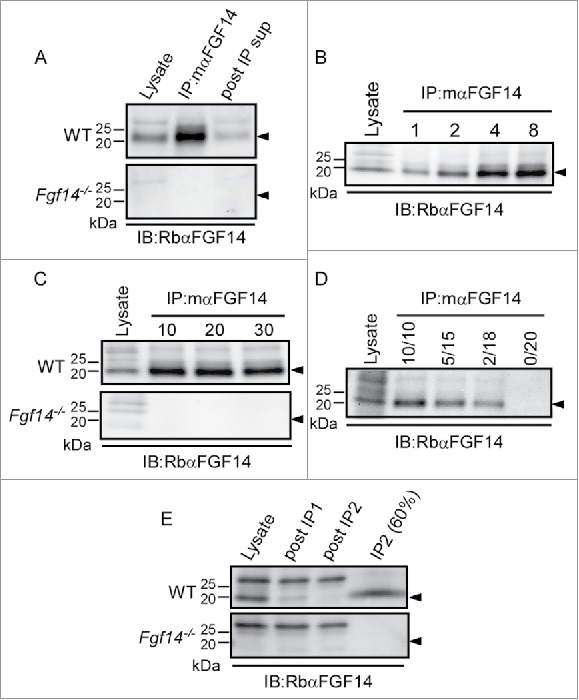
Optimization of mαFGF14 Immunoprecipitations. All blots were probed (IB) with a RbαFGF14 polyclonal antiserum as described in Materials and Methods. A. Representative Western blots of WT (top) and Fgf14−/− (bottom) cerebellar lysates, proteins immunoprecipitated with the mouse monoclonal anti-iFGF14 (mαFGF14) antibody, and the corresponding post immunoprecipitation supernatants (post IP sup). The ∼20 kDa iFGF14 protein is clearly evident in the WT lanes and absent in the Fgf14−/− lanes. Analyses of these blots revealed approximately 60% depletion of iFGF14 from WT mouse cerebellar lysates following IP with the mαFGF14 antibody. B. Western blots of WT cerebellar lysates before and after IP using variable amounts (1, 2, 4, or 8 mg) of protein lysates and a constant amount (20 μl) of mαFGF14-coupled sepharose beads. Analysis of IP samples revealed that increasing amounts of iFGF14 were immunoprecipitated from increasing amounts of cerebellar lysate, suggesting that the binding capacity of the mαFGF14 antibody-conjugated beads was not saturated. C. Western blots of WT (upper) and Fgf14−/− (lower) cerebellar lysates before and after IPs using 8 mg of cerebellar proteins with variable volumes (10, 20, or 30 μl) of mαFGF14 antibody-conjugated beads. Analysis of the IP samples revealed no significant increase in the amount of iFGF14 immunoprecipitated when the bead volume was increased. D. Western blot of WT cerebellar lysates and proteins immunoprecipitated from 8 mg of cerebellar proteins with decreasing volumes of mαFGF14 antibody-conjugated beads. Non-conjugated control sepharose beads were used to maintain the bead amount constant; the numbers above the lanes refer to the mαFGF14 antibody-conjugated bead volumes (left) and the control bead volumes (right). Decreasing amounts of iFGF14 were immunoprecipitated as the mαFGF14-antibody-conjugated bead volume was decreased. E. Western blots of WT and Fgf14−/− cerebellar lysates, post IP supernatants following sequential mαFGF14-IPs (post IP1 and post IP2), and proteins immunoprecipitated after IP2; 60% of the IP2 fraction was loaded onto the gel. Analysis of these blots revealed that approximately 85% depletion of iFGF14 was achieved with the first IP and a 90% depletion was achieved with the second IP.
