Figure 5.
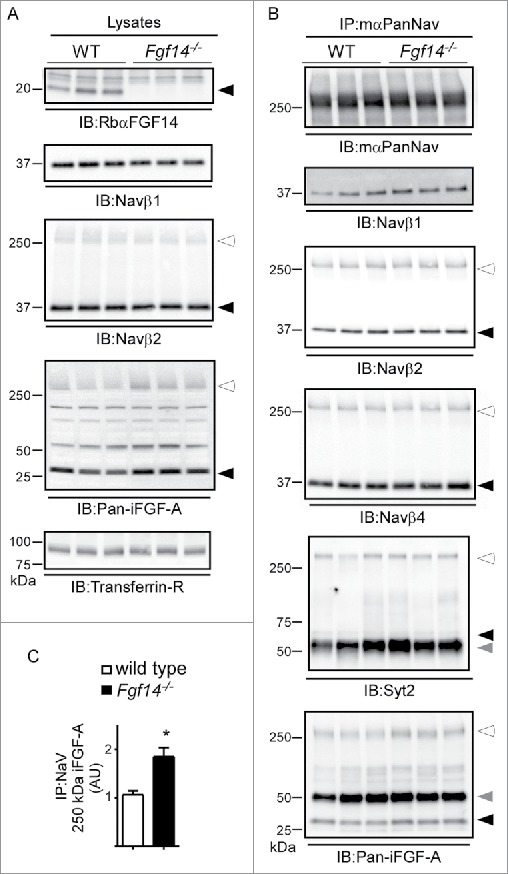
Western Blot Analysis of Nav Channel α Subunits and Nav Channel Interacting Proteins in WT and Fgf14−/− Cerebellar Lysates. A. Representative Western blots of cerebellar lysates from 3 WT and 3 Fgf14−/− animals. Immunoblots (IB) with the RbαFGF14 antibody identified iFGF14 in the 3 WT lanes but not the 3 Fgf14−/− lanes. IB with the anti-Navβ1 and anti-Navβ2 antibodies revealed no significant difference in the amounts of the Navβ1 and Navβ2 proteins in the WT and Fgf14−/− cerebellar lysates. IB with the anti-pan-iFGF-A antibody revealed no significant difference in A-type iFGF expression in WT and Fgf14−/− cerebellar lysates (see text). Closed arrowheads indicate dissociated protein bands and open arrowheads indicate proteins bound to Nav α subunits. B. Native Nav channel complexes were immunoprecipitated from the 3 WT and 3 Fgf14−/− cerebellar lysates depicted in using a monoclonal anti-PanNav α subunit-specific (mαPanNav) antibody and analyzed by Western blot. Similar amounts of Nav α subunit proteins immunoprecipitate from WT and Fgf14−/− cerebellar lysates with the mαPanNav antibody. IB with the anti-Navβ1, anti-Navβ2, anti-Navβ4 and anti-Syt2 antibodies revealed no significant differences in the amounts of the Navβ1, Navβ2, Navβ4 or Syt2 proteins that co-IP with the mαPanNav antibody from WT and Fgf14−/− cerebellar lysates. IB with the anti-Pan-iFGF-A antibody revealed that the amount of A-type iFGFs that co-IP with the mαPanNav antibody and that remain bound to Nav α subunits (˜250 kDa; open arrowhead) are greater in the WT, compared with the Fgf14−/−, cerebellar lysates. The gray arrowheads correspond to IgG heavy chain. C. Quantification of the intensities of the ˜250 kDa anti-Pan-iFGF-A bands, determined from blots such as those in (B), normalized to the amount of immunoprecipitated Nav α subunits in the same samples, revealed a significantly increased (*P<0.05) mean ± SEM band intensity in Fgf14−/−, compared to WT, IPs.
