Figure 2.
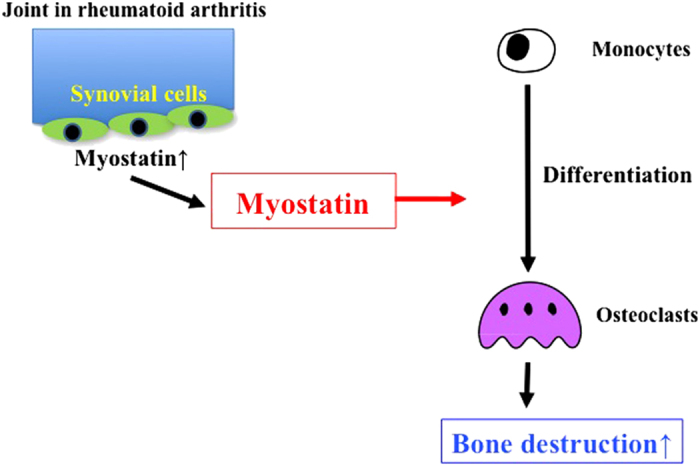
Role of myostatin in joint and bone destruction of rheumatoid arthritis. Exposure of synovial fibroblasts to inflammatory cytokines causes the upregulation of myostatin in patients with RA. Myostatin enhances RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in autocrine and paracrine manners. Myostatin stimulates osteoclast formation through increased Smad2-dependent nuclear translocation of NFATc1 and subsequent upregulation of osteoclast differentiation genes.13
