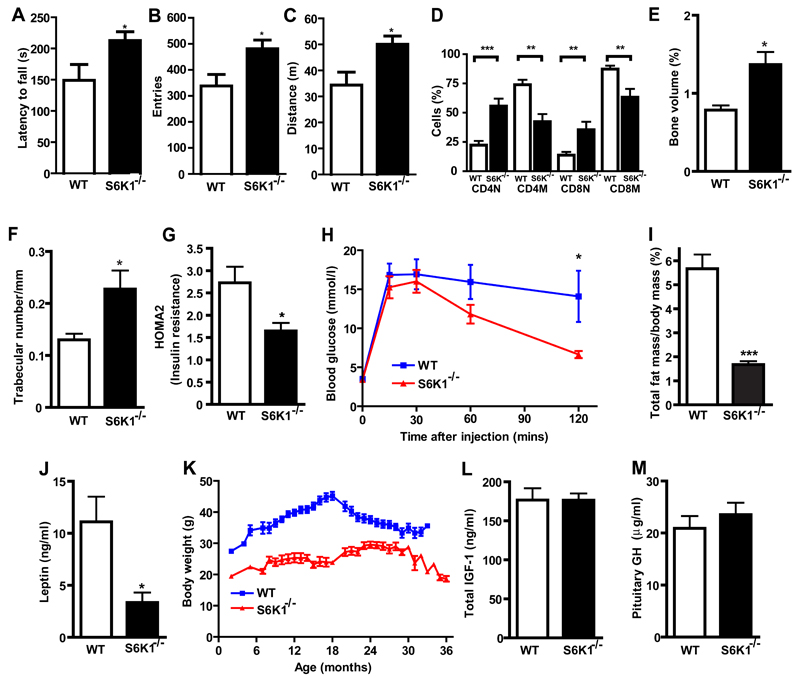
Fig. 2.
Age-related pathology and physiological characteristics of 600 day old female S6K1-/- mice. (A) S6K1-/- mice had improved rotarod performance. (B and C) Increased general activity and exploratory drive was observed in S6K1-/- mice. (D) Abundance of memory and naïve T cells in WT and S6K1-/- mice. (E and F) Bone volume and trabecular number in WT and S6K1-/- mice. (G and H) Insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance of WT and S6K1-/- mice. (I) S6K1-/- mice were lean and (J) had reduced plasma leptin levels. (K) Body mass (p< 0.01 at all time-points), total circulating IGF-1 (L) and pituitary GH concentrations in WT and S6K1-/- mice (M). Values are mean ± s.e.m. Asterisks indicate statistical difference compared to WT mice using two-tailed t-tests, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 and *** p<0.001. n= 6-8 per genotype.