Fig 2. The crossing scheme used to generate BY and YJM F2B6 NILs.
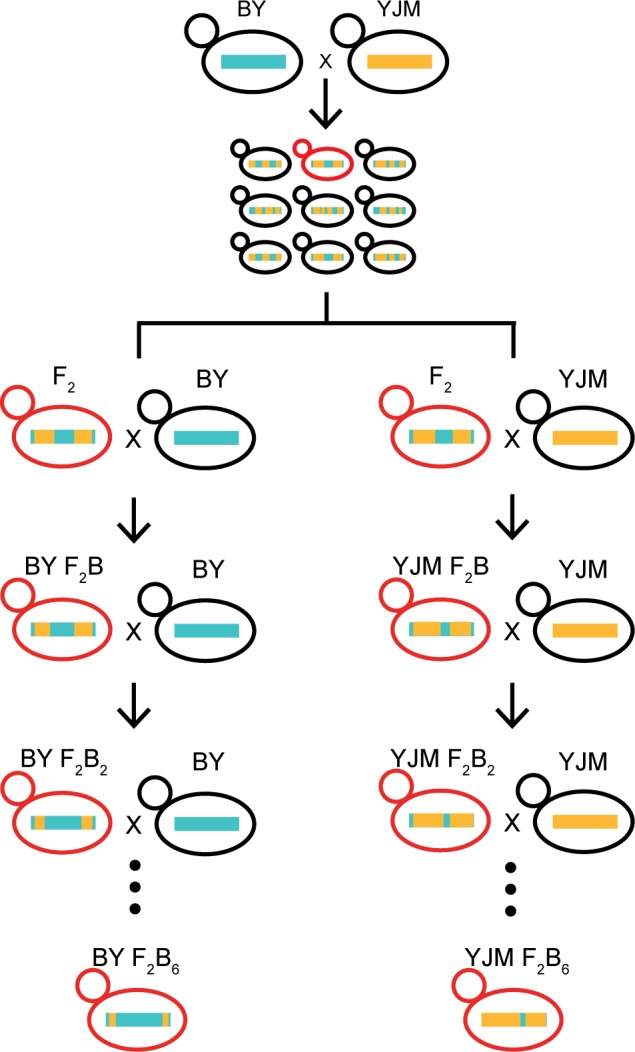
First, haploid versions of BY and YJM were mated, and the resulting F1 diploid was sporulated to generate haploid F2 segregants. These F2s were then screened for growth in E37. A single F2 exhibiting poor growth in E37 (shown in red) was chosen to serve as the progenitor for backcrossing. This F2 was then backcrossed to both BY and YJM, and the resulting diploids were sporulated to generate haploid F2B backcross segregants. Seven BY and seven YJM F2Bs that grow poorly in E37 were selected to serve as the progenitors for additional backcrossing. Next, these strains were subjected to five additional rounds of mating to the appropriate parent, sporulation, and selection for the poor growth phenotype to create 14 independent backcross lineages. Finally, a single haploid F2B6 exhibiting poor growth in E37 was chosen from each backcross lineage and designated as a Nearly Isogenic Line (NIL). These NILs are expected to carry combinations of alleles from one parent that collectively lead to poor growth in E37 when they co-occur in the genetic background of the other parent.
