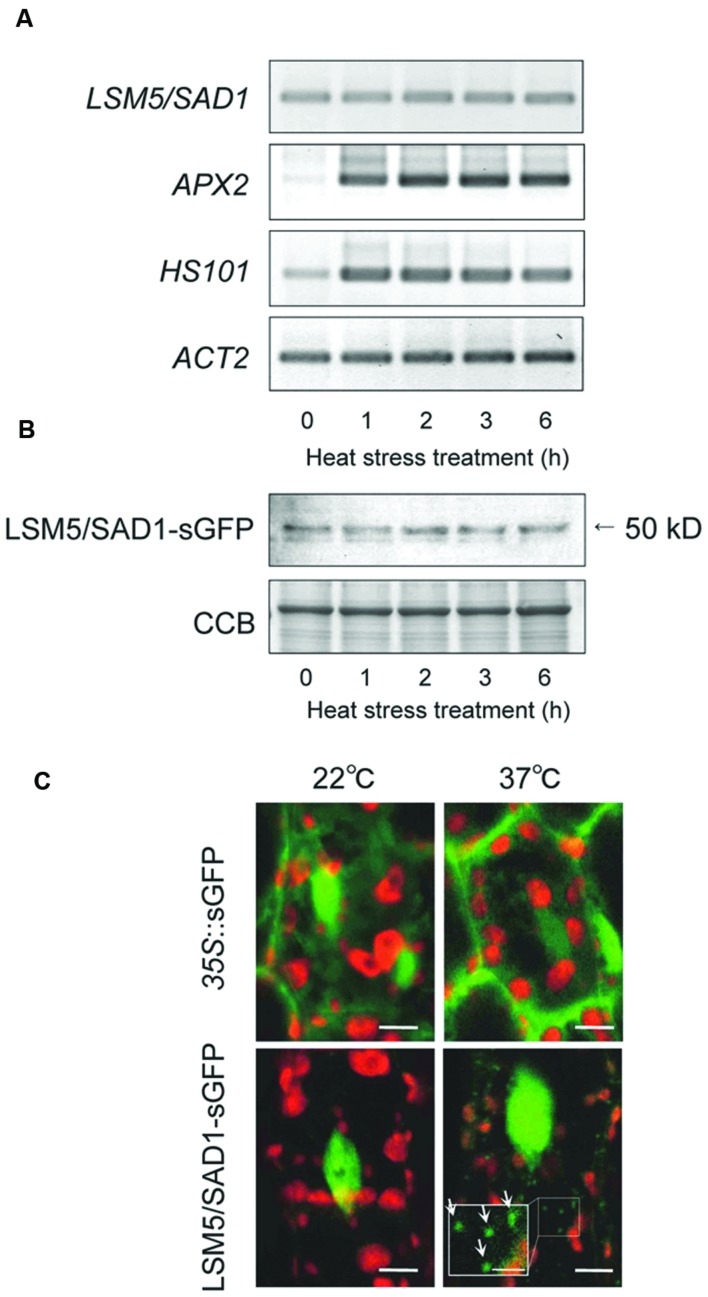
FIGURE 2.
Transcripts, protein levels and subcellular protein localization of LSM5/SAD1 during heat stress. (A) Expression patterns of LSM5/SAD1 and heat responsive marker genes, APX2 and HSP101, during heat stress in wild-type plants. ACT2 was used as an internal control. (B) Expression patterns of LSM5/SAD1-sGFP protein during heat stress. Transgenic plants expressing the LSM5/SAD1-sGFP fusion protein driven by the LSM5/SAD1 promoter were generated in the lsm5/sad1 mutant. This proLSM5/SAD1::LSM5/SAD1-sGFP construct complimented the phenotype of the lsm5/sad1 mutant. Twenty micrograms of total protein was loaded in each lane and immunologically detected using an anti-GFP antibody. Coomassie-stained portion (Cms) of gel is shown as a loading control. (A,B) 10-day-old seedlings were incubated at 37°C for 0, 1, 2, 3, and 6 h, and total mRNA and protein were extracted. (C) Confocal microscope images of the sGFP fluorescence of the proLSM5/SAD1::LSM5/SAD1-sGFP transgenic lsm5/sad1 plants and 35S::sGFP transgenic plants. The hypocotyl tissues were observed under the microscope before and after incubation at 37°C for 6 h. Green and red fluorescences indicate the sGFP signal and autofluorescence from the chloroplast, respectively. White arrows indicate cytoplasmic dots of LSM5/SAD1-sGFP fluorescence. Bars = 5 μm, whereas closed-up bar = 2.5 μm.