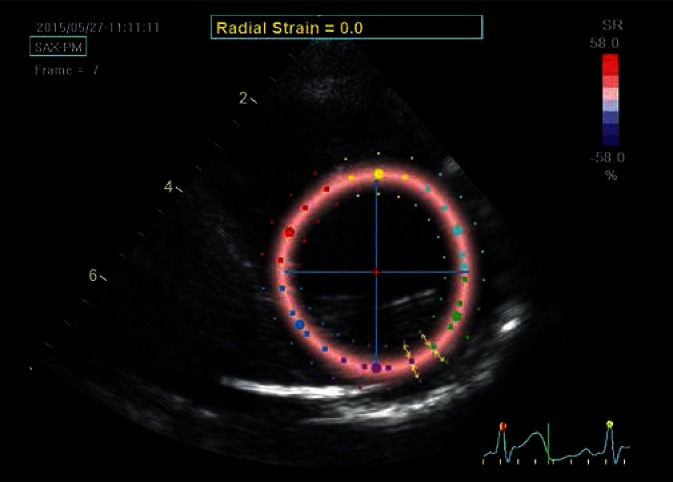
Fig. 4.
Parasternal transverse view of the left ventricle at the level of the papillary muscles; determination of the radial strain. Although the ROI is the same as for the circumferential strain, the strain is now analyzed perpendicular to lines delineating LV borders (arrows). In the case of systolic radial strain – as a result of ventricular wall thickening – speckles move away from each other and move closer during diastole, unlike the other strain components, which are brought closer to each other during systole. In order to maintain imaging uniformity, red color always codes for the expected direction of systolic strain, i.e. the color will indicate positive systolic radial strain values. The presented image was captured in the initial systolic phase, hence the uniform pale-pink color of the strain map