Figure 1. Local manipulation of histone modifications by TALE-HME affects alternative splicing of the target exon.
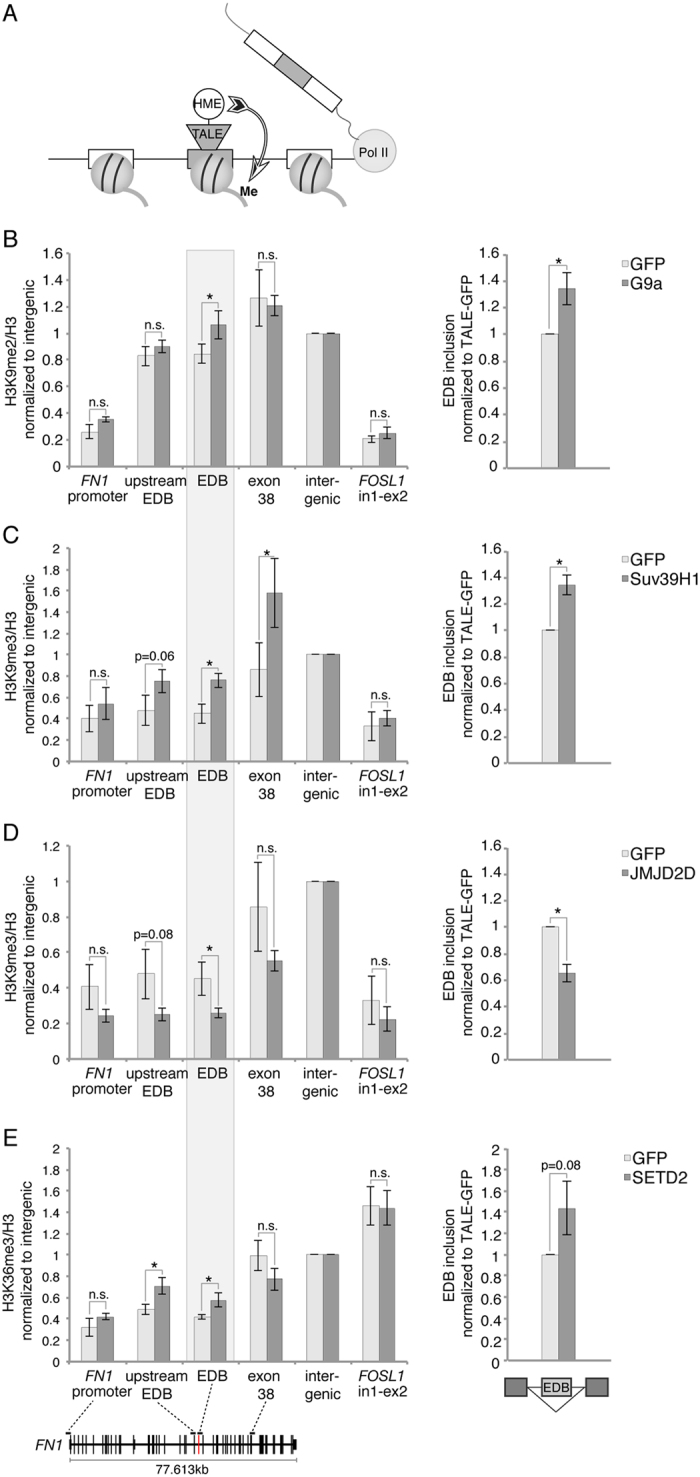
(A) Schematic representation of the approach. A TALE domain was assembled to bind the target exon and fused to HMEs. Upon binding of TALE-HME to the target exon, the local chromatin environment is modified. (B–E) Upon transient transfection with TALE-HME or TALE-GFP as a control, the effect on chromatin was monitored by ChIP (left panel) and EDB inclusion levels were assessed by RT-qPCR (right panel). ChIP signals are calculated as immunoprecipitated DNA over input signal and normalized to total H3 and an intergenic region on chromosome 10. Amplicon positions for FN1 are indicated in the gene diagram at the bottom. EDB inclusion rates are calculated as the ratio of the EDB exon to the upstream constitutive exon 24 and normalized to TALE-GFP. Mean ± SEM are shown, n = 3–4. Statistical significance of all results was analyzed by t-test and significant changes (p < 0.05) were indicated by * .
