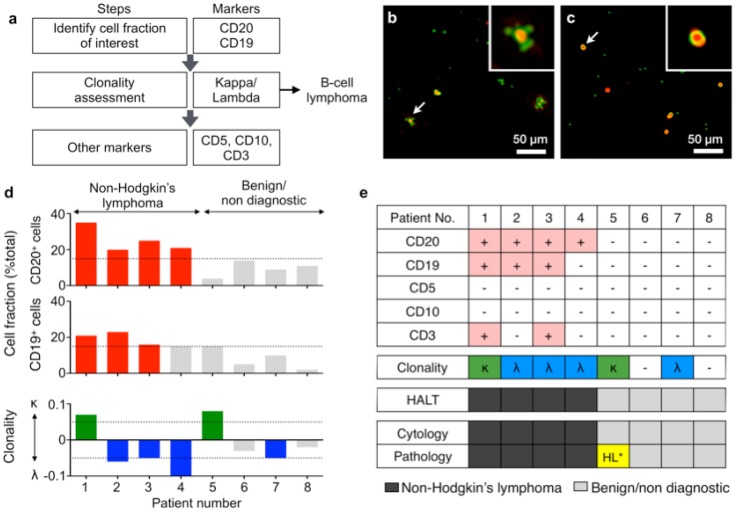
Figure 4.
Diagnosis with HALT platform in patients suspected with lymphoma. (a) Choice of markers and algorithm used for diagnosing non-Hodgkin lymphoma. (b, c) Representative composite images of cells from fine needle aspirates (FNAs) of patients with suspected lymphoma. Cells were immunolabeled with microbeads (4.5 μm) and imaged using HALT. Amplitude and phase contrast are pseudocolored to green and red, respectively. Insets are respective zoomed-in images of the cells highlighted with white arrows. Cells from NHL (non-Hodgkin lymphoma) exhibit increased bead binding (b) for the lymphoma marker, which is absent or comparatively less in sample obtained from benign adenopathy (c). (d) Sample consisting of more than 15% of a particular cluster designation (CD) marker was considered positive. The clonality of the population was determined by using the formula: (κ-λ)/(κ+λ) where κ and λ are average bead counts per cell for kappa and lambda light chains, respectively. Clonality was defined in the range of -1 to +1 where value >0 means kappa is more dominant while the value <0 means lambda is more prominent in the population. (e) FNAs from 8 patients were tested individually for a panel of relevant lymphoma biomarkers (CD20, CD19, CD5, CD10, CD3, kappa light chain, lambda light chain) and compared to pathology results. The results obtained from HALT platform were in concordance with flow cytometry and surgical pathology results. (HL: Hodgkin lymphoma).