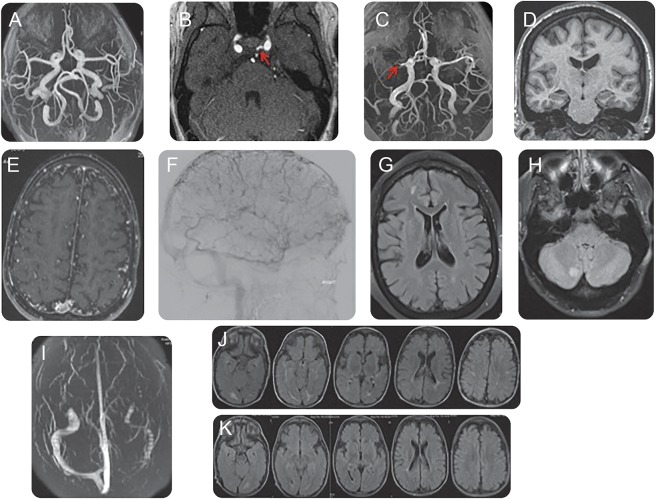
Figure. Neuroimaging manifestations of Cantú syndrome.
(A) Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of the head demonstrates dilated and tortuous arteries. (B) MRA of the head shows a left persistent trigeminal artery. (C) MRA of the head shows a right middle cerebral artery M1 division occlusion. (D) MRI T1-weighted without contrast shows mild right hemispheric atrophy. (E) MRA of the head demonstrates an abundance of distal collateral vessels. (F) Cerebral arteriogram shows an abundance of distal collateral vessels. (G) MRI brain T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) shows subcortical white matter changes. (H) MRI brain T2-weighted FLAIR shows white matter lesion in the right cerebellum. (I) Magnetic resonance venography of the head demonstrates aplasia of the left transverse sinus. (J) MRI brain T2-weighted FLAIR shows subcortical white matter lesions predominantly in the posterior circulation with (K) subsequent improvement/resolution of the white matter lesions on follow-up MRI brain T2-weighted FLAIR.