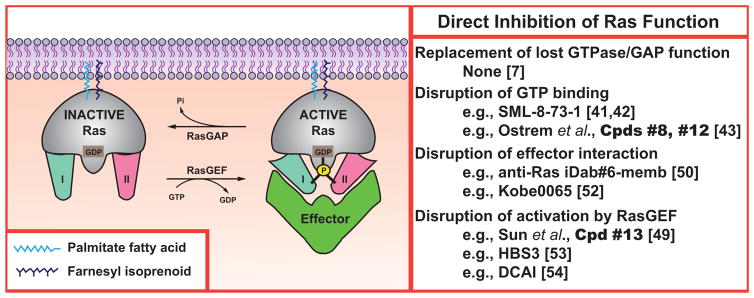
Fig. (1). Direct inhibition of Ras Function.
The Ras activation/deactivation cycle and interaction with downstream effectors provides several potential therapeutic targets. Mature Ras proteins are anchored at the membrane and achieve an active conformation that interacts with effectors following the binding of GTP. This active conformation is lost upon GTP hydrolysis.