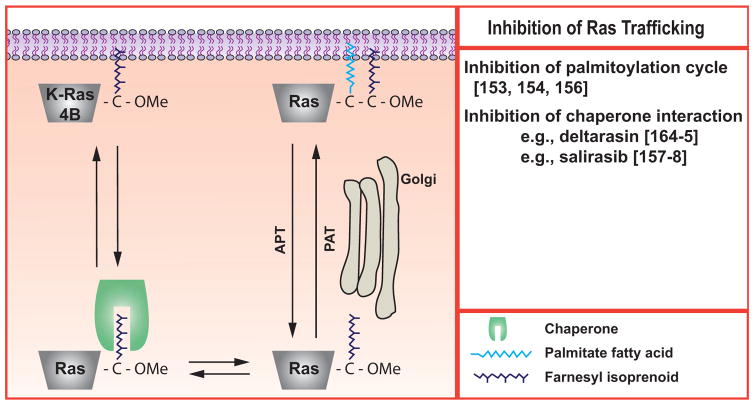
Fig. (3). Inhibition of Ras trafficking.
The prenylated Ras proteins require additional steps to achieve the membrane localization that is required for their activity. H-Ras, K-Ras4A, and N-Ras are reversibly palmitoylated. K-Ras4B requires interactions with chaperone proteins such as galectins or PDEδ. This figure is adapted and re-drawn from [156].