Fig. 10.
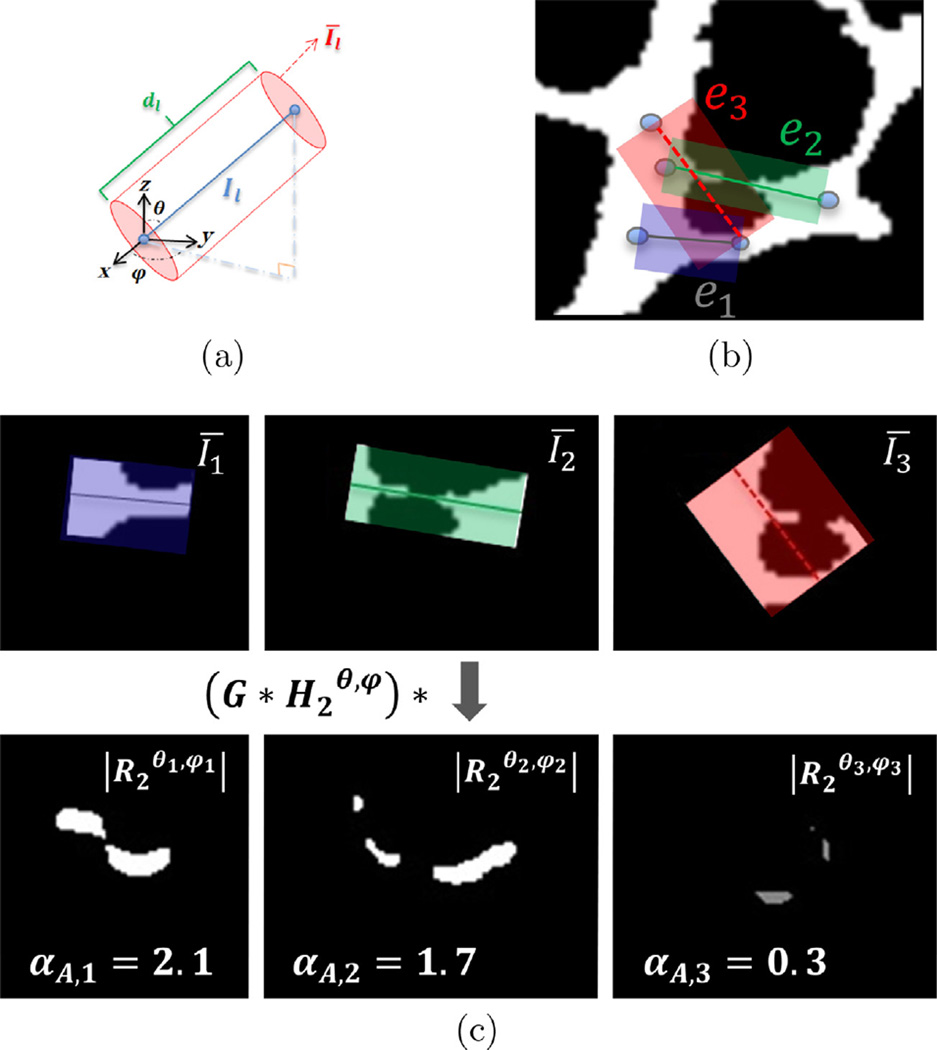
(a) Spherical coordinates θ and ϕ of edge el along with other terms used for the directional filtering concept are shown in a Cartesian system. (b) An example consisting three different scenarios of the edge layouts on a vascular structure is provided. The utilities of e1 (which clearly passes through a vessel) and e2 (which is well aligned with the local direction of vasculature) are both higher than that of e3 (which is poorly aligned with the vasculature and passes through a good deal of the background). (c) Three ROIs of the edges (top) and the absolute value of the directionally filtered ROIs and their alignment term, αA,l, with respect to each edge’s direction (bottom). The edge e3 that is not aligned with the vasculature in its ROI has the smallest alignment value.