Figure 4. Differences among the networks of the three PHG clusters.
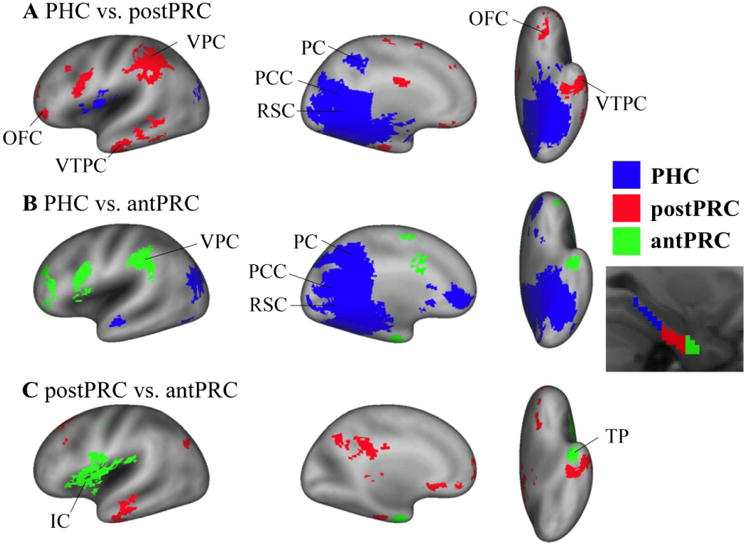
Paired t-tests were conducted to identify significant differences among the three networks for the three PHG clusters (i.e. PHC, postPRC, and antPRC) (cluster corrected p< .05). A) Differences between the PHC network and the postPRC network. Blue voxels represent significant voxels in the PHC network comparing with the postPRC network (PHC > postPRC). Conversely, red voxels represent significant voxels in the postPRC network comparing with the PHC network (postPRC > PHC). B) Differences between the PHC network and the antPRC network. Blue voxels represent significant voxels in the PHC network comparing with the antPRC network (PHC > antPRC). Green voxels represent significant voxels in the antPRC network comparing with the PHC network (antPRC > PHC). C) Differences between the postPRC network and antPRC network. Red voxels are the significant voxels in the postPRC network comparing with the antPRC network (postPRC > antPRC). Green voxels are the significant voxels in the antPRC network comparing with the postPRC network (antPRC > postPRC). IC: insular cortex. OFC: orbitofrontal cortex. PC: precuneus. PCC: posterior cingulated cortex. RSC: retrosplenial cortex. TP: temporal pole. VPC: ventral parietal cortex. VTPC: ventral temporopolar cortex.
