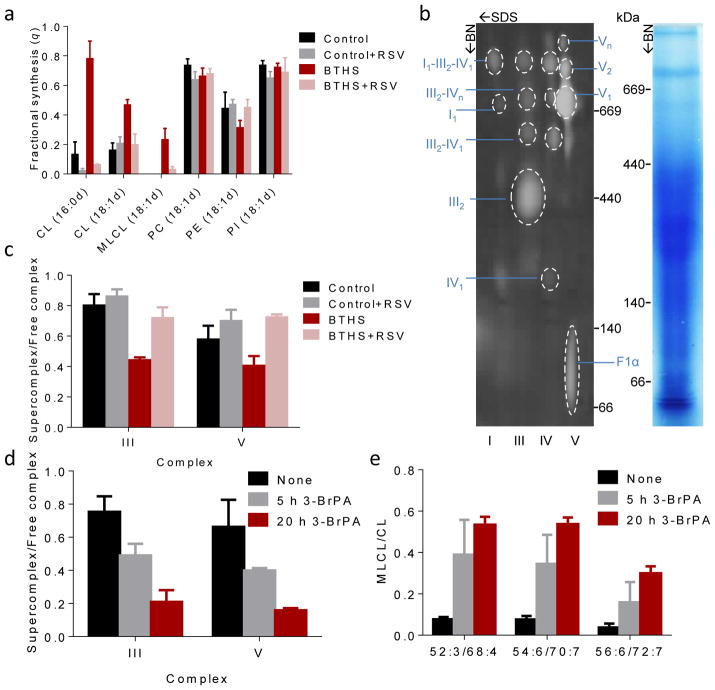
Figure 5. Supercomplexes protect CL from degradation.
(a) Human lymphoblasts were cultured ±40 μM RSV for 36 hours. The fractional syntheses of lipids were determined by incorporating 2H-labeled palmitic acid (16:0d) or oleic acid (18:1d) for 8 hours. RSV inhibited the turnover of CL in BTHS (P<0.03) but not in controls. RSV had no effect on other phospholipids. (b–c) Lymphoblast mitochondria were solubilized with digitonin, separated by 2D-Blue Native/SDS-PAGE, and analyzed with primary antibodies to NDUFB6 (complex I), UQCRC2 (complex III), MtCO1 (complex IV), and F1α (complex V). The Coomassie-stained lane shows the BN-PAGE separation and the 2-D blot shows individual complexes and supercomplexes with the positions of molecular weight markers. BTHS decreased the proportion of supercomplexes, RSV increased it back to normal (P<0.02). (d–e) Control lymphoblasts were treated with 80 μM 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA) for 5 or 20 hours. 3-BrPA decreased the proportion of supercomplexes and increased the MLCL/CL ratio (P<0.03). Data (means±s.e.m., N=3) were analyzed by t-test (a, c) or ANOVA (d, e).