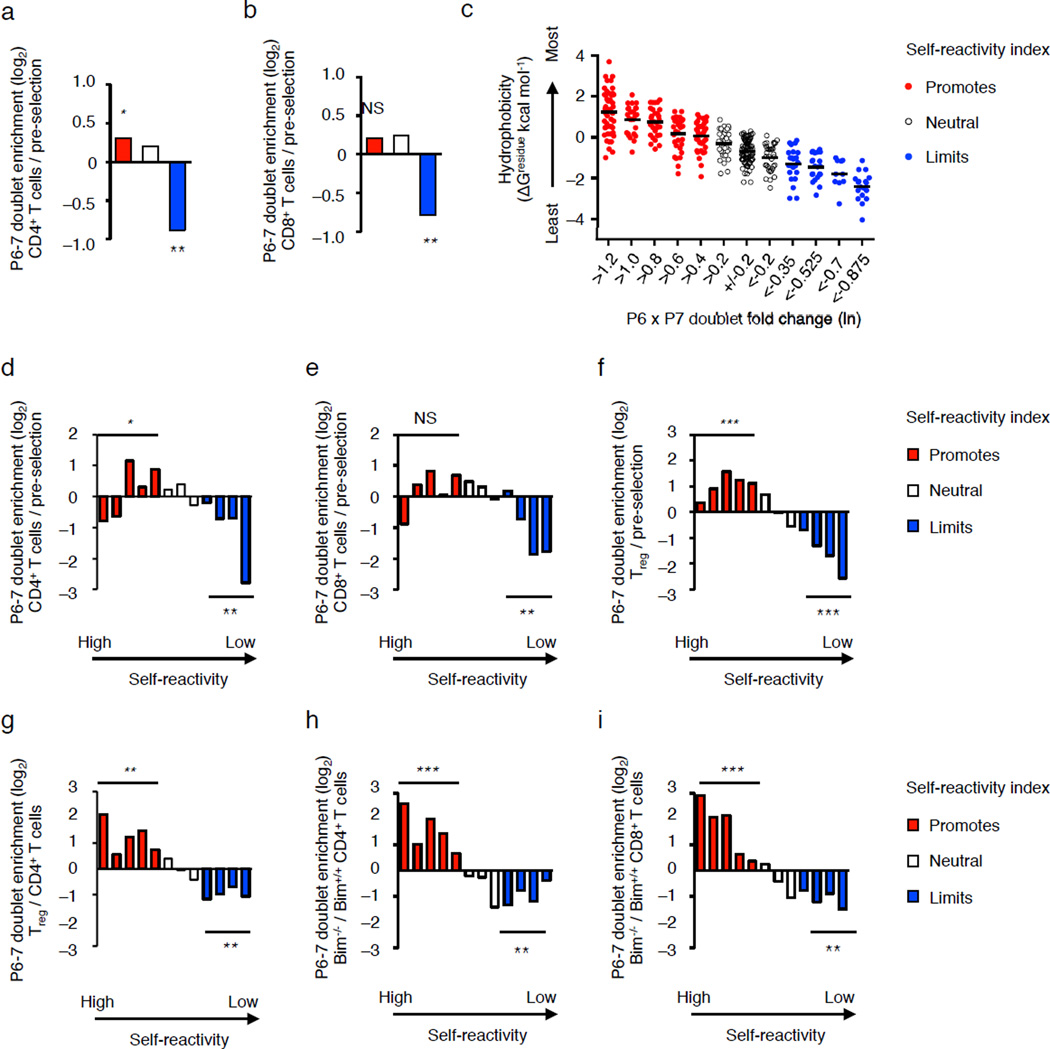
Figure 7.
Thymic selection biases the CDR3β P6–7 doublet usage of mature Vβ2+, Vβ6+ and Vβ8.2+ T cells. (a,b) Fold change in the number of differentially expressed doublets that promote (red), are neutral (white) or limit (blue) self-reactivity among naïve CD4+ (a), and CD8+ T cells (b) in C57BL/6 mice as compared to pre-selection DP thymocytes. (c) Average interfacial hydrophobicity of CDR3β P6–7 doublet partitioned into 12 groups based on e0.2-fold changes in the self-reactivity, each dot represents a particular CDR3β P6–7 doublet. (d–f) Fold change in the number of differentially expressed doublets for naïve CD4+ T cells (d), naïve CD8+ T cells (e) or Treg cells (f), compared to pre-selection thymocytes. (g–i) Fold change in the number of differentially expressed doublets for Treg cells (f) or Bim−/− CD4+ T cells compared to C57BL/6 CD4+ T cells, and (i) Bim−/− CD8+ T cells compared to C57BL/6 CD8+ T cells. NS, not statistically significant, *P < 10−4, **P < 10−10, ***P < 10−25 (hypergeometric test, all red or all blue doublets compared to total population). Data are summation derived from Vβ2+, Vβ6+ and Vβ8.2+ TCRs with CDR3β loops of 11–17 amino acids, obtained by the average frequencies from three independent biological replicates (a,b,d–i). (c) Bar represents average hydrophobicity within the group.