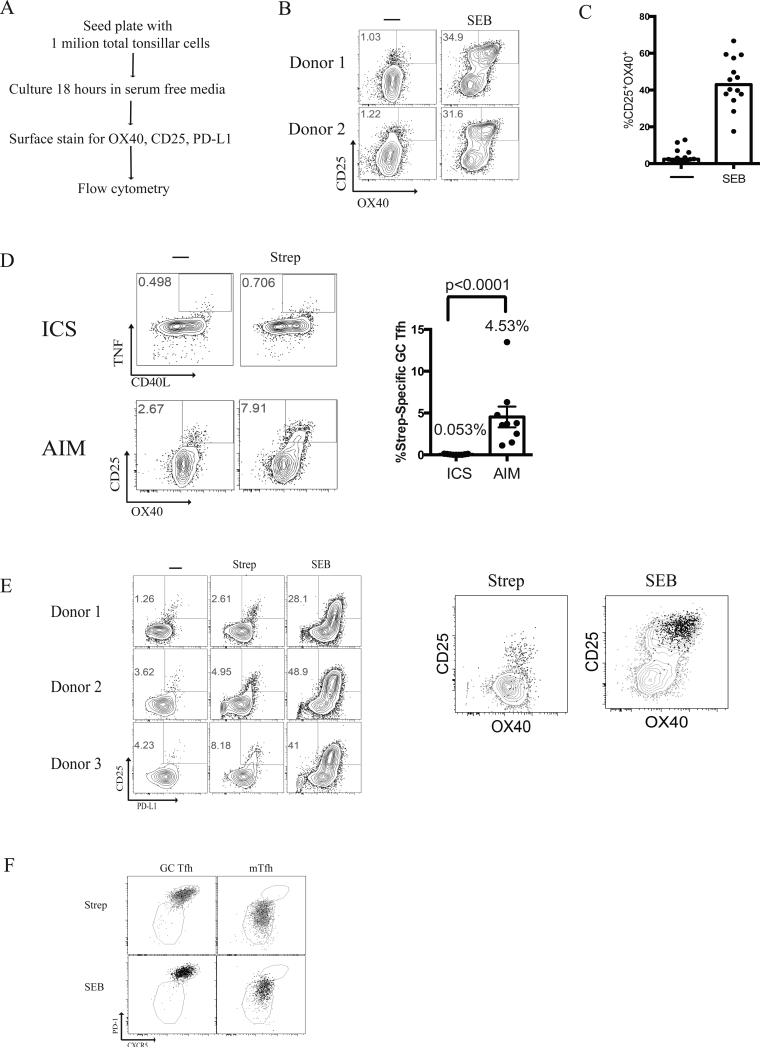
FIGURE 3.
Activation Induced Marker induction by GC Tfh cells. (A) Experimental design for human tonsillar AIM assay (B) Representative flow cytometry plots of CD25+OX40+ upregulation by live GC Tfh cells (CXCR5hiPD-1hiCD45RA−CD4+) from 3 different tonsils following 18 hours stimulation with 1μg/mL Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). (C) Median CD25+OX40+ expression by live GC Tfh cells following stimulation with SEB. Data are from 14 samples from 2 independent experiments. The response by antigen-specific cells was background subtracted for each donor. (D) Comparison of Strep-specific GC Tfh by ICS (TNF+CD40L+) and AIM (CD25+OX40+). The % Strep-specific GC Tfh responses were background subtracted. Data are from 9 samples from 2 independent experiments. The response by antigen-specific cells was background subtracted for each donor. (E) CD25+OX40+ GC Tfh cells are also PD-L1+. Representative FACS plots of CD25+PD-L1+ co-expression following stimulation with either Strep or SEB. Strep-specific PD-L1+CD4+ GC Tfh cells (black contour plot) were overlaid onto Strep-specific CD25+OX40+ GC Tfh cells (grey dots). SEB responsive PD-L1+CD4+ GC Tfh cells (black contour plot) were overlaid onto SEB responsive CD25+OX40+ GC Tfh cells (grey dots). Data are from 14 samples from 2 independent experiments. (F). Representative flow cytometry overlay plots demonstrating CD25+OX40+ cells (black dots) within each sorted population (grey dots) for each condition (Strep-stimulated, and SEB-stimulated). This is representative of 3 independent experiments consisting of 7 donors.