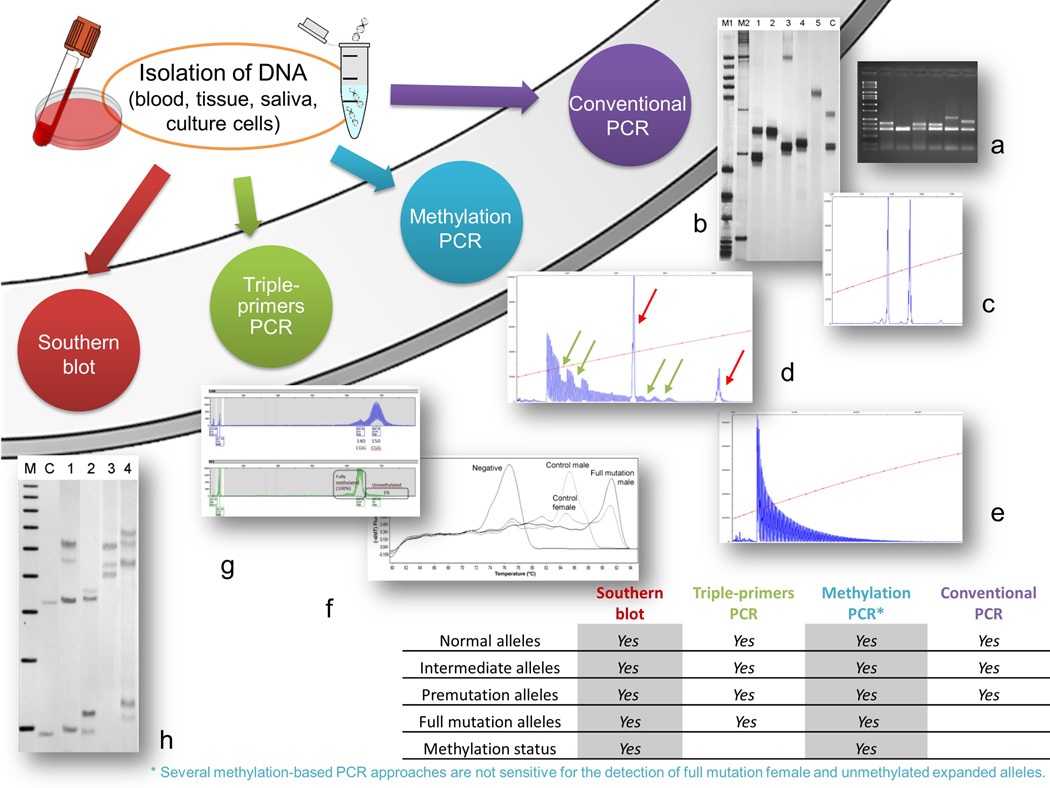
Figure 1.
Diagram showing the different methodologies utilized for the diagnosis of FXS. Genomic DNA (gDNA) can be isolated from whole blood, tissue, saliva or culture cells. Isolated gDNA can be amplified by PCR or digested with methylation sensitive restriction enzymes for Southern blot analysis. Conventional PCR using primers that flank the CGG repeat can amplify FMR1 alleles containing CGG repeat usually up the lower premutation range. The alleles can be visualized either on an agarose gel (a), on an acrylamide gel (b) or by capillary electrophoresis (CE) (c). CE provides accurate CGG sizing particularly if a CGG size marker is utilized. Triple primer PCR (d= premutation female; e= full mutation male) utilizes two FMR1 specific primers that flank the CGG repeat as well as a third primer that is complementary to the CGG repeat element (CGG primer). The PCR produces both full-length gene-specific FMR1 amplicons (red arrows in d) as well as triplet repeat-specific products visualized on CE as a series of peaks (d, e). Two AGG interruptions within the CGG repeat are visible, both within the normal and the premutation allele (green arrows in d) from a woman premutation carrier. Methylation status (including measure of the percent of methylation for any given allele, percent of cells carrying a methylated allele or measure of the activation ration in females) can be assessed by various mPCR strategies (g, mPCR-CE,(47); f, MM-RTPCR, modified from (69)) or by Southern blot analysis (h). Southern blot analysis (h) is performed using genomic DNA digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and NruI and separated on agarose gel. The DNA is transferred to a nylon membrane and then hybridized with the dig labeled specific FMR1 probe, StB12.3 (46). M= marker; C= normal control female; lane 1= full mutation female; lane 2= premutation female; lane 3= full mutation male; lane 4= mosaic male. The table in the right lower corner shows the information that can be obtained by the various PCR-methodologies. Specifically, the detection of normal, intermediate, premutation and full mutation alleles, can be obtained using any of the indicated approaches except that full mutation alleles are not amplifiable using conventional PCR. Southern blot can detect alleles from the normal throughout the full mutation range; however, sizing is obtained only for full mutation alleles.