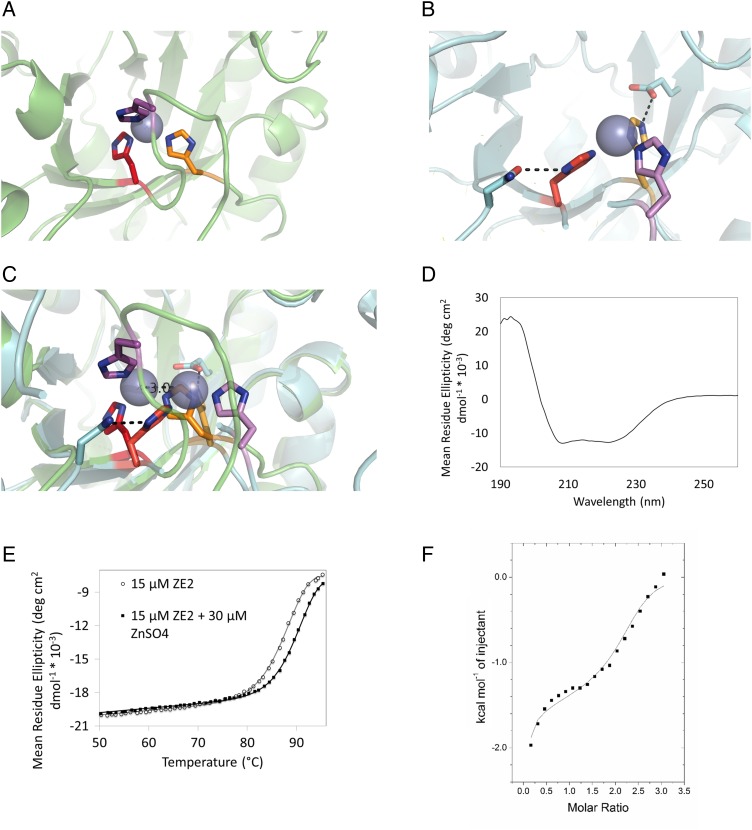
Fig. 2.
(A) Predicted structure of ZE2 zinc binding site. (B) Crystal structure of ZE2 zinc binding site. (C) Crystal structure of ZE2 overlaid with the design model. Although the predicted residues do form the zinc binding site, the histidines (along with the zinc ion) have shifted their positions to form stabilizing hydrogen bonds with surrounding residues. H210 (bottom center) has changed rotamers to form a hydrogen bond with the side chain of E50; H179 (left) has changed rotamers to form a hydrogen bond with N160 and is coordinating the zinc ion with the epsilon nitrogen instead of the delta nitrogen; and the loop containing H183 (top center, far right) has moved over 9 Å to accommodate the new position of the binding site. (D) ZE2 is well folded in the absence of zinc. (E) ZE2 shows increased thermal stability in the presence of saturating zinc, which increases the thermal transition temperature from 90.2 to 92.4°C. (F) ZE2 binds zinc in the designed site with 1.4 µM affinity as measured by ITC. A second nonspecific binding event (KD = 92 µM) is also observed by ITC, but only the first site appears in the crystal structure.