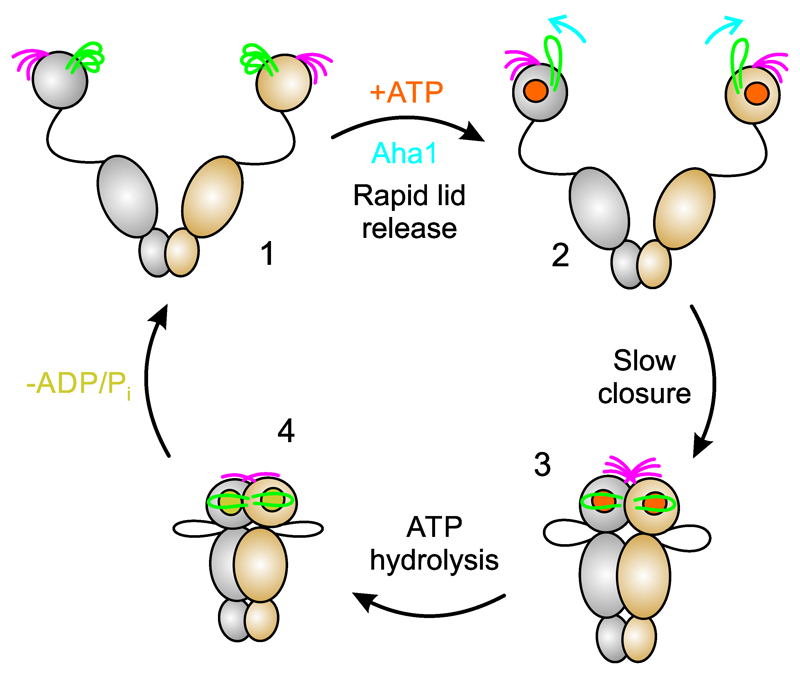
Figure 6. Integration of results into the chaperone catalytic cycle.
(1) At the beginning of the catalytic cycle, apo Hsp90 populates a heterogeneous ensemble of open-clamp conformers. Lid (green) and N-terminal β-strand (magenta) are highly mobile structural elements with sub-millisecond reconfiguration times. (2) Binding of ATP to the NTD leads to rapid release of the lid to an intermediate conformational state. The co-chaperone Aha1 pre-associates N- and M-domains but also remodels the lid segment for accelerated closure. (3) Closure of the molecular clamp involves cooperative action of conformational switches. Closure of the lid over the ATP-binding pocket, cross-subunit swap of β-strands, and association of the N- and M-domains are slow and interdependent. Swap of the terminal β-strands is weakly coupled with the other motions. (4) Hydrolysis of ATP leads to a compact, ADP-bound conformation, which relaxes to an open state with concomitant release of ADP and inorganic phosphate. Opening of the molecular clamp reconstitutes Hsp90 for the next catalytic cycle.