Figure 1.
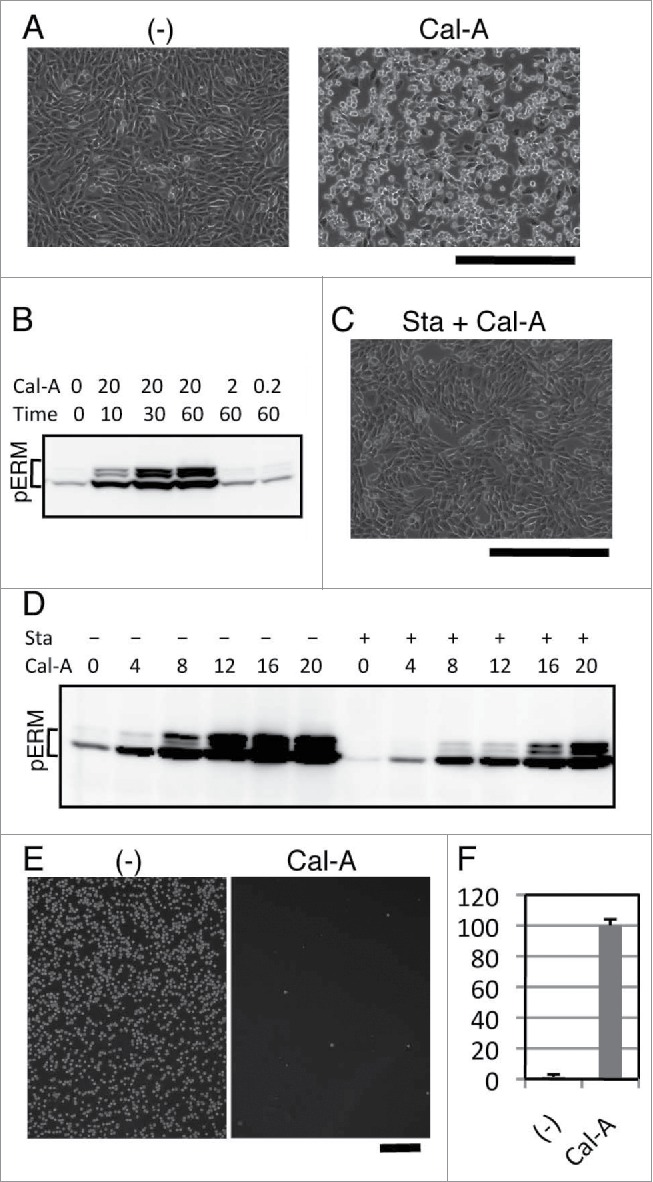
Effect of Calyculin A (Cal-A) on cell shape, ERM phosphorylation and inhibition of cell reattachment in NIH3T3 cells. (A) Cal-A treatment induced cell rounding in NIH3T3 cells. Cell bodies of flat cells were retracted within 30 min after incubation with 20 nM Cal-A. Magnification: x100. Scale bar: 400 μm. (B) Immunoblotting with anti-phospho-ERM Ab. Detection of phosphorylated ERM proteins (pERM) dramatically increased over time after the addition of Cal-A. Concentration of Cal-A: nM, time: min. (C) Suppression of Cal-A-induced NIH3T3 cell rounding by Staurosporine (Sta). Image of cells incubated for 30 min with 10 nM Cal-A after 50 nM Staurosporine pretreatment is shown. Staurosporine pretreatment delayed Cal-A-induced cell rounding. Magnification: x100. Scale bar: 400 μm. (D) Suppression of Cal-A-induced ERM phosphorylation by Staurosporine. Pretreatment with 50 nM Staurosporine was described by +, while concentrations of Cal-A (nM, 1h incubation) were also described. Staurosporine decreased phospho-ERM in Cal-A-treated and untreated cells. E: Inhibition of cell reattachment to substrate by Cal-A treatment. Detached NIH3T3 cells were re-incubated with or without 10 nM Cal-A then washed. Images of cells remained attached after wash are demonstrated. Magnification: x40. Scale bar: 400 μm. F: Ratios of unattached cells per total cells are demonstrated by percentage.
