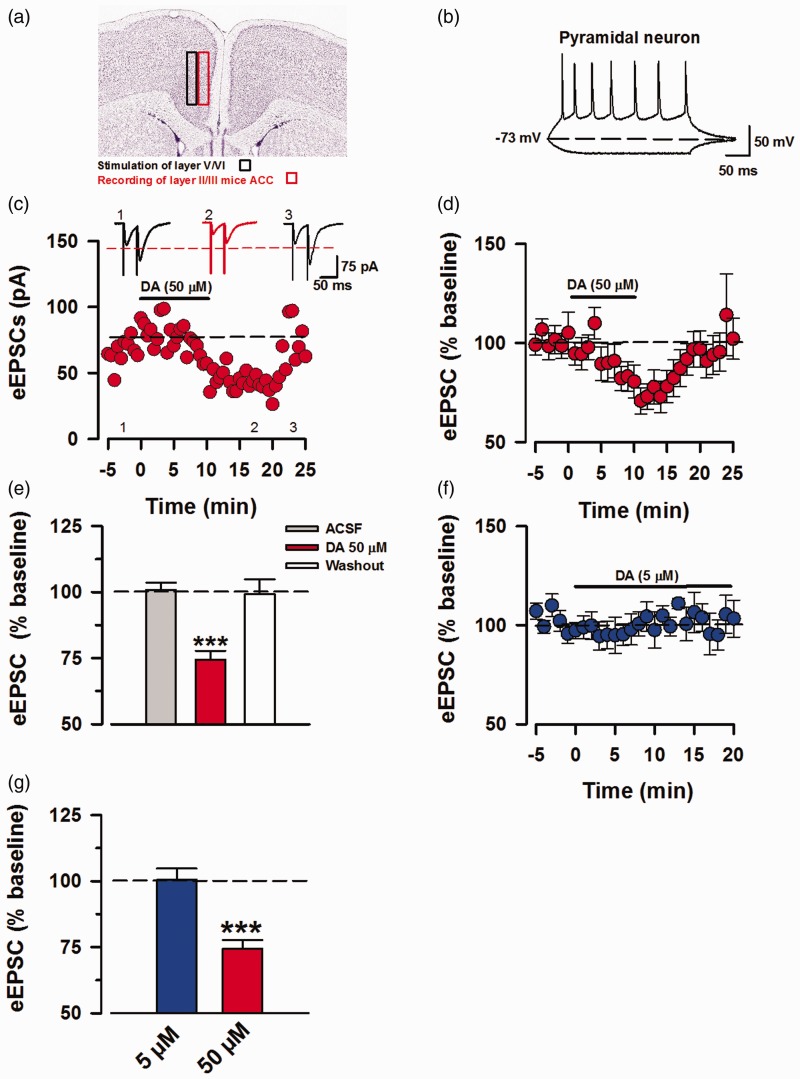
Figure 1.
Perfusion of high dose DA inhibits ACC pyramidal eEPSCs. Voltage-clamp whole-cell recordings of eEPSCs in pyramidal neurons of layer II/III of mice ACC. (a) Representative diagram of recording location at layer II/III and stimulation of layer V/IV in mice ACC, image credit: Allen Institute, mouse coronal brain atlas, version 1:2008, coronal level 43. (b) Sample action potential firing pattern of pyramidal neuron in current-clamp mode by injection of 15 mV currents for 400 ms, every 15 s. (c) Sample EPSC trace of AMPA/KA currents in layers II/III, depicting the time course for reduction of EPSC amplitude due to DA interaction with DARs and recovery after washing out DA. The AMPA/KAR currents were recorded in presence of PTX (100 μM). (d) Averaged and normalized (%) of eEPSCs (n = 11/8 mice). (e) Inhibition induced by DA (50 μM) was statistically significant in comparison to the baseline and washout (one-way ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). (f) Averaged and normalized (%) of eEPSCs showing no inhibition in response to DA (5 μM; blue, n = 5/4 mice). (g) Results for statistical analysis of DA (5 μM) against baseline (t-test, P = 0.65), data shown in comparison to DA (50 μM). Statistical analyses were performed for 5 min bins. Error Bars represent SEM. eEPSCs: evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents.