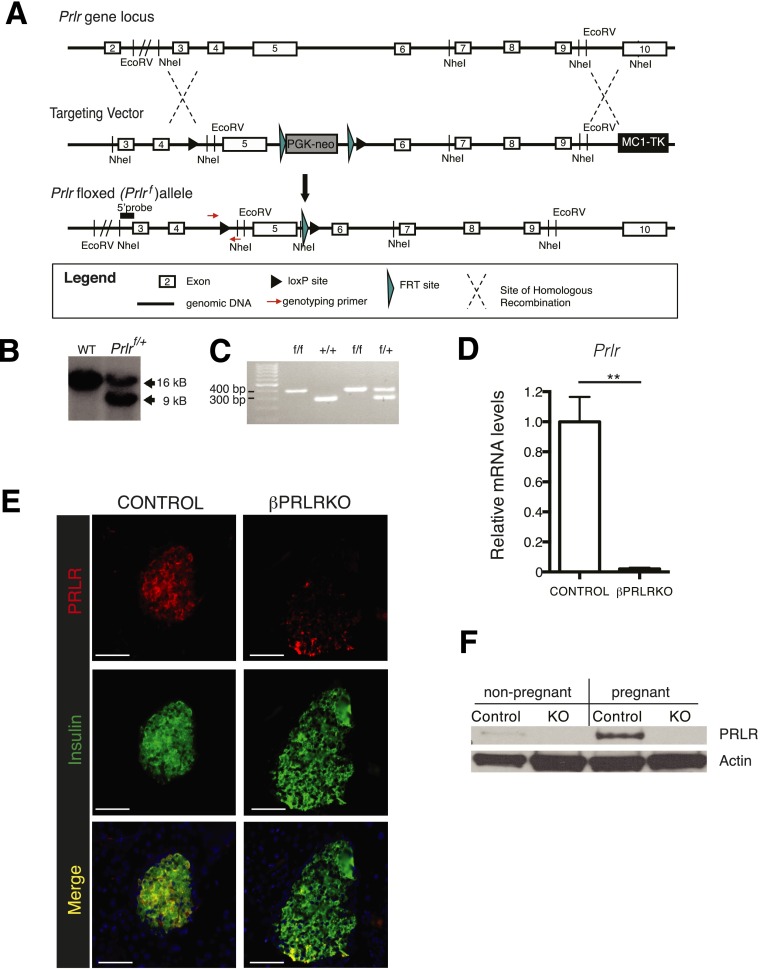
Figure 1.
Conditional inactivation of PRLR signaling in pancreatic β-cells (βPRLRKO). A: Schematic diagram (not to scale) depicting the Prlr gene locus, targeting vector sequence, and Prlrf allele structure (see research design and methods). B: Southern blot of genomic DNA from mice demonstrating germline transmission of Prlrf. Introduction of a NheI site downstream of the loxP cassette resulted in a 9-kb (targeted allele) rather than a 16-kb fragment (wild-type [WT] allele). C: Genotyping PCR of a litter depicting representative progeny of all potential Prlr genotypes following a cross of Prlrf/+ mice. D: mRNA levels of Prlr in βPRLRKO females (RIP-Cre;Prlrf/f) and control littermates (Prlrf/f). n = 6 mice/group. E: Immunofluorescence images of islets from βPRLRKO female and control mice stained for PRLR and insulin (scale bar, 100 μm). F: Western blot of PRLR expression from islets isolated from virgin βPRLRKO female and controls. Actin was used as a loading control. **P ≤ 0.01 by t test.