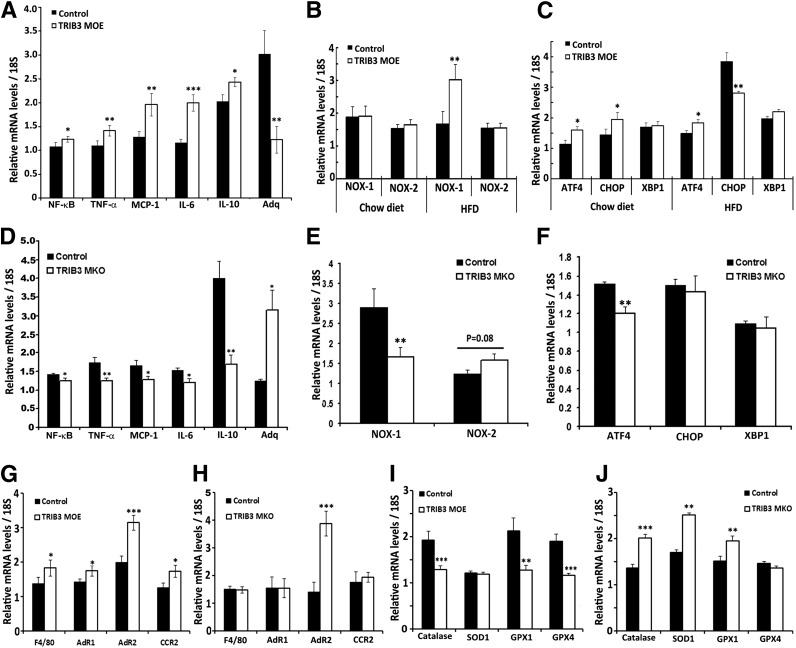
Figure 7.
Opposite expressions of genes in inflammation, ROS production, and stress pathways in TRIB3 MOE and TRIB3 MKO mice. A: Increased NF-κB expression, elevated proinflammatory cytokines (TNF- α, MCP-1, IL-6, IL-10), and decreased anti-inflammatory cytokine Adq in skeletal muscle of TRIB3 MOE mice. B: ROS-producing gene NOX-1 but not NOX-2 expressions were significantly increased in skeletal muscle of TRIB3 MOE mice under HFD (nutrient excess condition). C: Increased ATF4-CHOP transcription in TRIB3 MOE mice, with a potential feedback inhibition on CHOP expression under the HFD condition. D: Decreased intramuscular inflammatory profile in TRIB3 MKO mice. E: ROS-producing gene NOX-1 was significantly decreased in TRIB3 MKO mice fed the HFD. F: Decreased endothelium reticulum stress gene ATF4 in skeletal muscle of TRIB3 MKO mice fed the HFD. G and H: Expressions of macrophage marker F4/80 and chemokine receptors (AdR1, AdR2, CCR2) in skeletal muscle of TRIB3 MOE and MKO mice fed the HFD. I and J: Expressions of critical antioxidants (catalase, SOD1, GPX1, and GPX4) in skeletal muscle of TRIB3 MOE and MKO mice fed the HFD. Real-time PCR was done in soleus muscle (n = 6). Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 vs. control group by Student t test.