Figure 4.
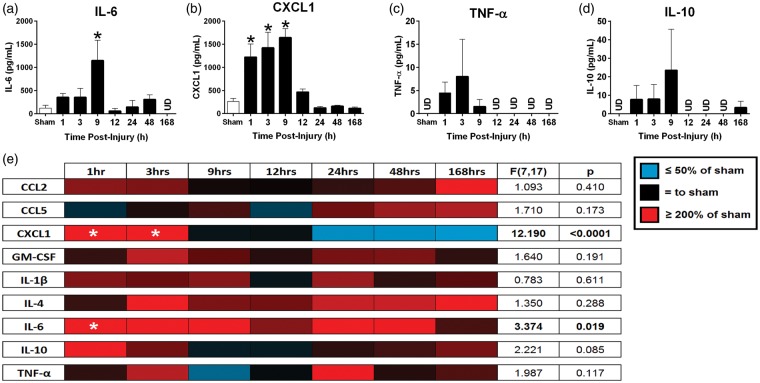
TBI initiated a central and peripheral inflammatory response. Cortical cytokine and chemokine levels were measured by multiplex ELISA following TBI (a-d). Acute increases in proinflammatory (a) IL-6 and (b) CXCL1 were significant in comparison to uninjured sham levels (n = 3–5, mean ± SEM). Serum cytokine and chemokine levels were measured for nine chemokine and cytokine analytes at seven time points following diffuse TBI (e). Proinflammatory CXCL1 and IL-6 were significantly elevated compared to sham during the acute phase following injury (n = 3–5). Although the levels for the remaining molecules changed with respect to sham, the differences were not significant in comparison to sham. Color gradations indicate the protein levels compared to sham, where reds are increased levels and blues are decreased levels.
TBI: traumatic brain injury; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; IL6: interleukin 6; CXCL1: chemokine ligand 1.