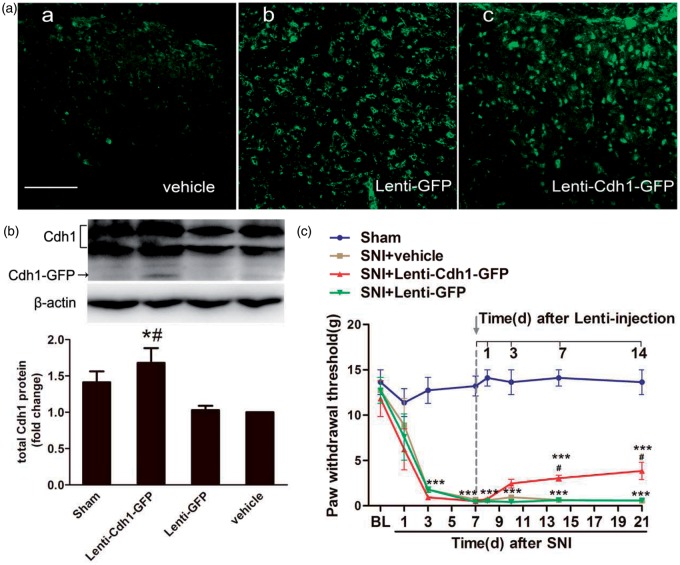
Figure 3.
Effects of intrathecal administration of recombinant lentivirus encoding Cdh1 (Lenti-Cdh1-GFP) on mechanical allodynia in the ipsilateral hind paws of SNI-treated rats. (a) GFP immunostaining was obviously observed in the superficial laminae of the dorsal horn at three days after intrathecal injection of Lenti-Cdh1-GFP (4.0 × 108 TU/mL; 10 µL) (c) and control lentivirus (Lenti-GFP; 4.0 × 108 TU/mL; 10 µL) (b), but not vehicle (0.9% saline;10 µL) (a). (b) Representative bands (top) for the expression of Cdh1 in the spinal cord of rats at three days after intrathecal injection of Lenti-Cdh1-GFP, Lenti-GFP or vehicle. Quantitative data (bottom) for Western blotting bands (n = 3 in each group) are shown. *P < 0.05 versus Lenti-GFP; #P < 0.05 versus vehicle; one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. Note that the fusion protein of Cdh1–GFP was detected in the spinal cord tissues at three days after Lenti-Cdh1-GFP infection. (c) MWTs of ipsilateral hind paws to von Frey filament probing were measured before and at 1 day, 3 days, 7 days and 14 days after intrathecal treatment with Lenti-Cdh1-GFP, Lenti-GFP or vehicle. Intrathecal administration of recombinant lentivirus was performed immediately after behavioural determinations on day 7. Data were expressed in mean ± SEM (n = 6 in each group). ***P < 0.001 versus sham; #P < 0.05 versus SNI + vehicle; two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. BL: baseline. Scale bars: 100 µm.