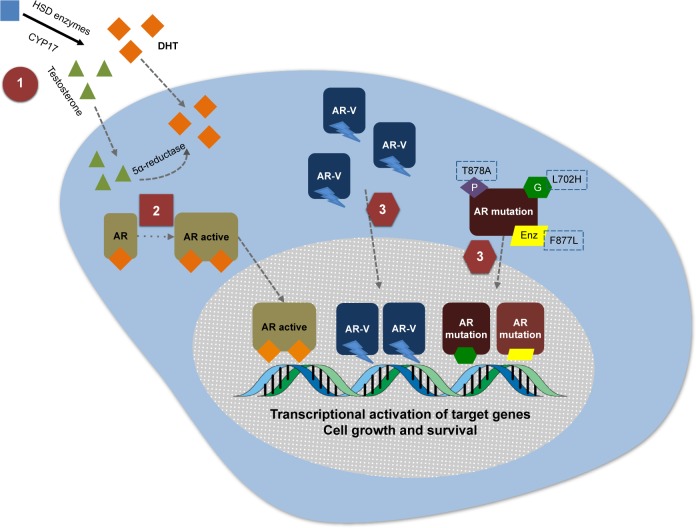
Figure 1.
Three mechanisms of action of galeterone.
Notes: This figure highlights the androgen receptor (AR) activation axis, with conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the 5α-reductase enzyme, and subsequent AR activation, dimerization, nuclear translocation and activation of transcriptional activation of target genes. The figure also demonstrates potential mechanisms of resistance to AR therapies, including the development of AR splice variants (AR-V) and AR mutations. Finally, it highlights galeterone’s mechanisms of action in each of these AR signaling pathways implicated in resistance to novel androgen/AR-directed therapies: 1) CYP lyase inhibition; 2) AR antagonism to both full-length and mutant AR; and 3) degradation of the AR, including AR splice variants.
Abbreviation: Enz, enzalutamide.