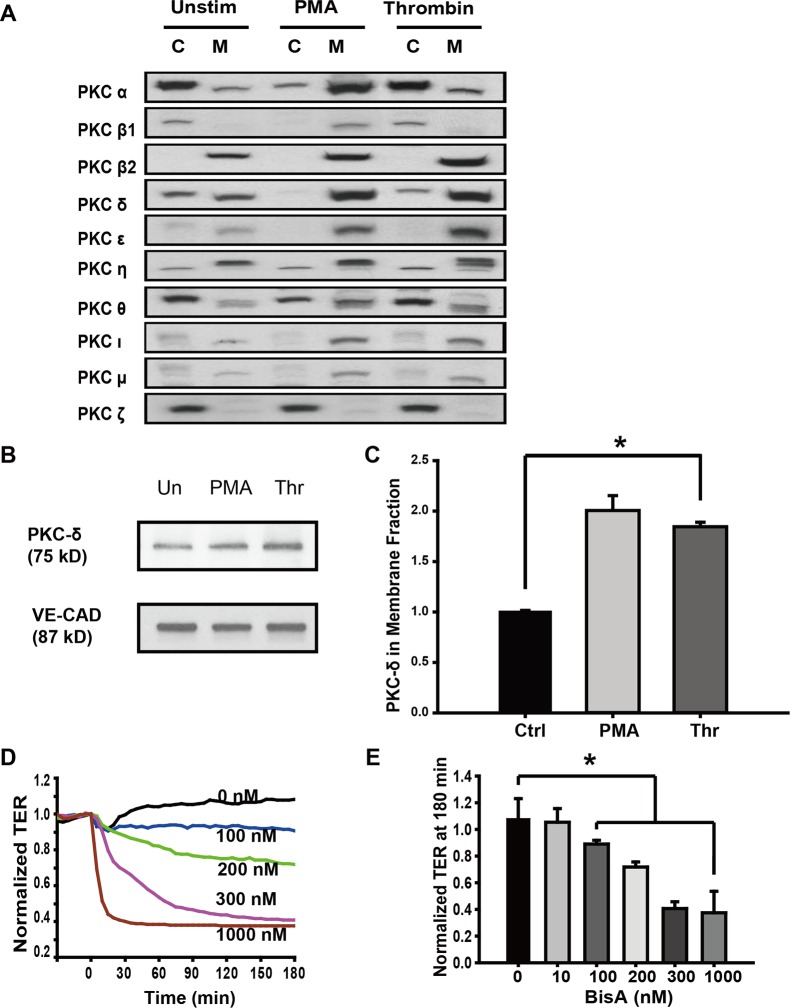
Fig 1. The role of PKCδ in thrombin-induced endothelial barrier disruption.
(A) Cells were treated with thrombin (1 U/ml, 15 min) or PMA (100 nM, 30 min) with unstimulated cells (Unstim) used as controls. Cytosolic (C) and membrane (M) fractions were immunoblotted with various anti-PKC isoform-specific antibodies. Both thrombin and PMA increased PKCδ in the membrane fraction and correspondingly decreased it in the cytosol fraction thereby indicating that PKCδ is activated and translocated to membranes. (B) Cells were treated as Fig 1A, Membrane fractions were immunoblotted with PKCδ and VE-Cadherin specific antibodies. (C) Normalized densitometry of PKCδ in membrane fraction is shown (n ≥ 3/condition, * p < 0.05). (D) Human pulmonary artery EC were grown to full confluency on gold microelectrodes and then treated with 100–1000 nM BisA, a putative activator of PKCδ. BisA induced a dose-dependent decrease in TER corresponding to increased permeability. Representative traces are shown. (E) TER values in BisA-treated cells at 180 min are shown (n = 4/condition, * p < 0.05 compared to control).