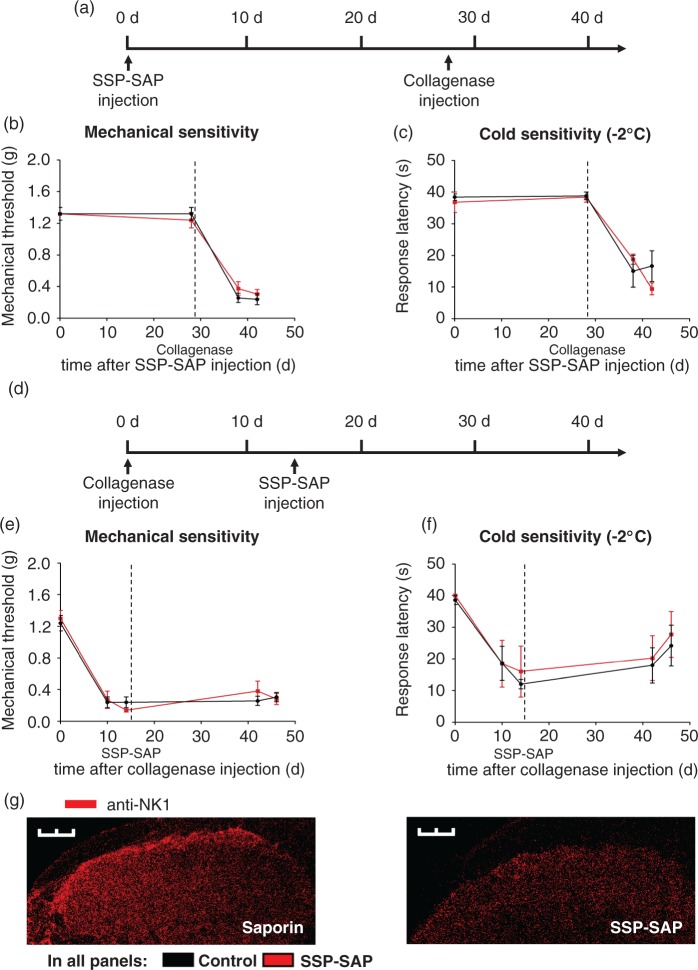
Figure 4.
Ablation of lamina I/III NK1 receptor positive neurons in the spinal cord does not affect induction or maintenance of hypersensitivity associated with thalamic collagenase injection. (a) Timeline of spinal NK1 receptor positive neuron ablation by intrathecal SSP-SAP injection and induction of hypersensitivity by thalamic collagenase injection. (b, c) SSP-SAP treatment 28 days prior to thalamic collagenase injection does not prevent development of mechanical (b) or cold (c) hypersensitivity as compared to the corresponding SAP treated control mice. (d) Timeline showing the time points of hypersensitivity induction by thalamic collagenase injection and pharmacological intervention by intrathecal SSP-SAP injection. (e, f) Mechanical (e) and cold (f) hypersensitivity is maintained to a similar degree in SSP-SAP injected animals and controls. (g) Immunohistochemistry with anti-NK1-receptor antibody demonstrating SSP-SAP induced ablation of lamina I NK1 receptor positive neurons in the spinal cord. Scale bar: 300 µm. Data were analyzed via repeated measures ANOVA, post-hoc Fisher’s test in b–f; n = 4–5 mice per group; *P < 0.05 compared to controls.