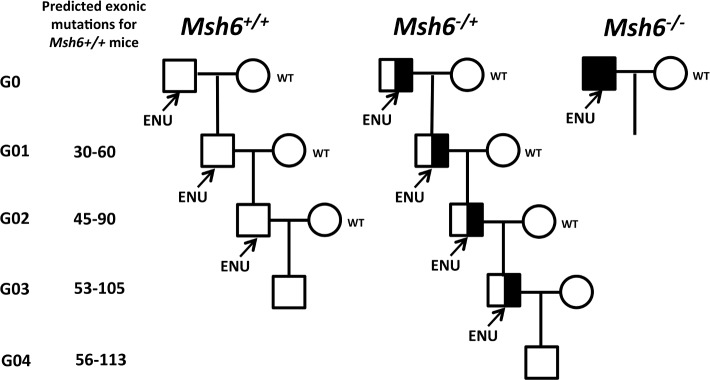
Fig 1. Breeding scheme for analysis of serial ENU-treatment in wild-type and MMR defective mice.
G01 males carry a random set of de novo point mutations induced by ENU treatment of wild-type or MMR-mutant G0 mice. G02, G03 and G04 carry mutations that were induced in their respective parents, as well as those inherited from previous generations. Each generation treated with ENU will on average have 3000–6000 new ENU-induced variants genome wide. After ENU treatment each male is crossed with a wild-type female; their progeny will inherit newly induced mutations and 50% of those of the parent. The mutations are sampled by exome analysis; the expected number of ascertained mutations (E) is shown. The ENU treatment was performed on three successive generations for the Msh6+/+ mice and four generation for the Msh6+/- mice. Msh6-/- mice did not tolerate ENU treatment.