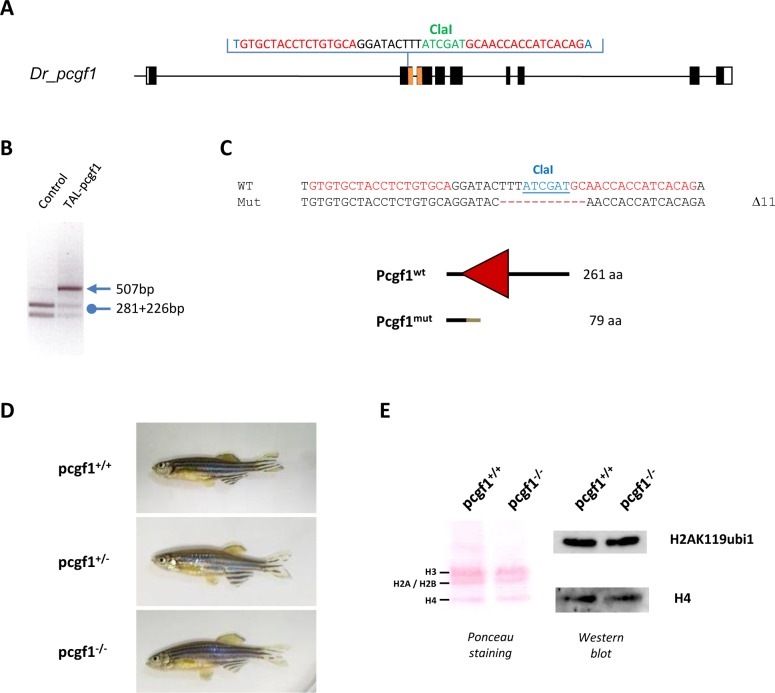
Fig 3. Generation of a pcgf1 mutant line using the TALEN technology.
(A) Schematic representation of the genomic structure of the pcgf1 gene, with coding and untranslated exon depicted as solid and open boxes, respectively. The exonic regions coding for the conserved RING finger motif are shown in orange. The location of the pcgf1 TALEN in exon 2 is indicated. The pcgf1 TALEN target sequence with Left and Right TALEN binding sites in red is shown. The ClaI restriction site is indicated in green. (B) Identification of mutant embryos using a diagnostic restriction. Genomic DNA was prepared from an uninjected (Control) and a pcgf1 TALEN injected (TAL-pcgf1) embryo. The TALEN targeted DNA region is amplified by PCR and subjected to ClaI digestion. The TAL-pcgf1 injected embryo contains undigested material (arrow at 507 bp), indicating that the ClaI diagnostic restriction site has been disrupted. (C) Sequence of the mutant allele compared to its wild-type counterpart. Dashes indicate deleted nucleotides. For the peptide sequence, the gray line indicates residues read out of frame prior to encountering a premature stop codon and the red triangle corresponds to the RING finger motif in the wild-type protein. Size of the predicted proteins is indicated. (D) Pictures of siblings from a pcgf1+/- x pcgf1+/- cross at 7 months. The genotype of the fish was established using the ClaI diagnostic restriction on genomic DNA obtained by fin clipping. (E) Global monoubiquitinylation of histone H2A is not affected in pcgf1-/- mutants. Total histone from pools of 5 embryos at 7 dpf were extracted and analyzed by western blotting. The efficiency of the transfer on the membrane is verified by Ponceau staining (Left) before incubation with anti-H2AK119ub1 and anti-H4 antibodies (Right).