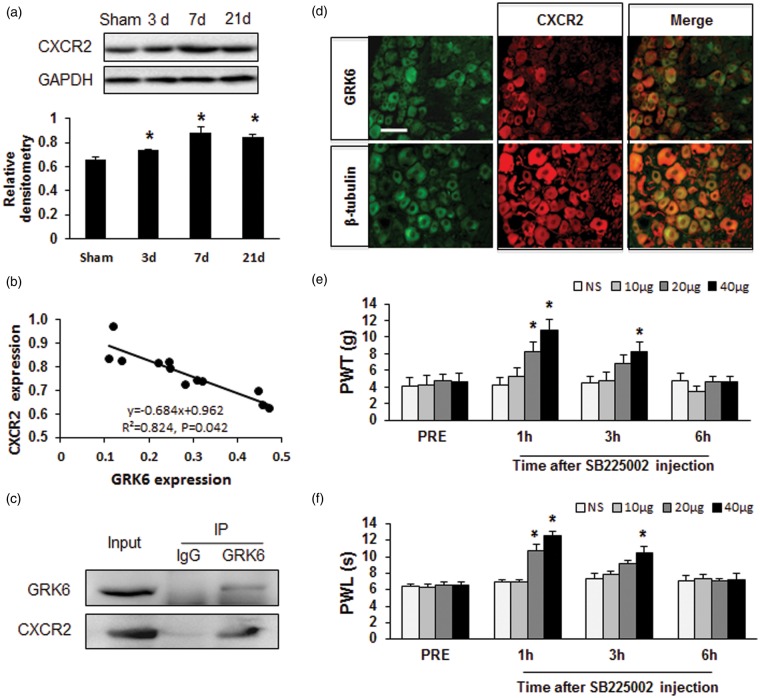
Figure 6.
Correlation of GRK6 and CXCR2 expression and attenuation of neuropathic pain by CXCR2 inhibitor. (a) Expression of CXCR2 protein in DRGs was increased from day 3 to day 21 following CCI. *p < .05 vs. Sham. (b) Correlation analysis showed that the alternations of CXCR2 and GRK6 following CCI were negatively correlated. r2 = 0.824, p = .042. (c) Co-immunoprecipitation showed the co-localization of CXCR2 and GRK6 in DRGs in CCI rats. (d) Immunofluorescence analysis showed CXCR2 was co-expressed in GRK6 positive DRG neurons. GRK6-positive cells (top left) and β-tubulin-positive cells (bottom left) shown in green. CXCR2-positive cells were shown in red (middle column). Merge of double labeling of GRK6 and CXCR2 (top right) and merge of β-tubulin positive staining and CXCR2 labeling (bottom right). Scale bar = 50 µm. (e, f) Administration of the selective CXCR2 antagonist SB225002 mitigated mechanical hyperalgesia and heat hyperalgesia in CCI rats. Antinociceptive effects of a single intrathecal (it.) injection of 20 µg SB225002 were observed at 1 h and disappeared at 2 h. Antinociceptive effects induced by a single injection of SB225002 at 40 µg were observed at 1 h and disappeared 6 h after injection. Injection of SB225002 (10 µg, i.t.) did not alter the PWT and PWL of CCI rats. N = 6 rats for each group, *p < .05, compared to NS group. PWL: paw withdraw latency; PWT: paw mechanical withdrawal thresholds.