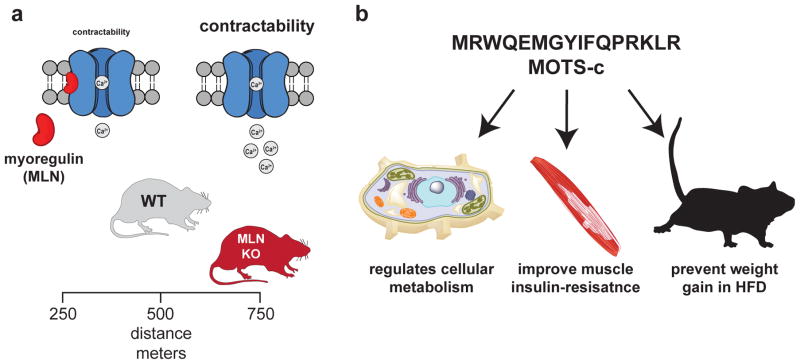
Figure 5. smORFs with functions in mice.
a) Myoregulin (MLN) is a sarcolamban homolog that is restricted to the skeletal muscle of mammals. This SEP binds and inhibits the SERCA calcium channel to affect calcium flux and, therefore, calcium contraction in the muscle. Loss of myoregulin increases contractibility and this improves endurance as myoregulin knockout mice (MLN KO) run longer and significantly further than their wild type (WT) counterparts. b) MOTS-c is a newly discovered SEP that is produced from a smORF found on mitochondrial RNA. Cellular and physiological studies identified some biological functions for MOTS-c, such as regulation of cell metabolism. When administered to mice MOTS-c improves muscle insulin resistance and can prevent weight gain and the onset of metabolic disease in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD).