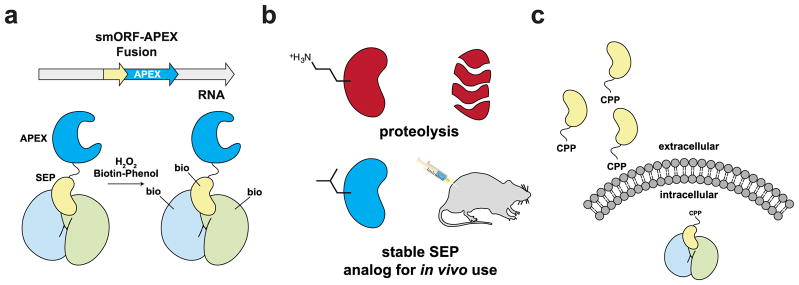
Figure 6. The possible impact of chemical biology in smORF/SEP research.
a) Functional SEPs appear to operate through protein-protein interactions (PPIs). The characterization of new SEPs will benefit from proximity labeling methods such as APEX oxidation of a biotin phenol to generate a reactive intermediate that labels nearby proteins to identify PPIs in cells. SEP-APEX fusions will help identify SEP-protein complexes, providing key information in characterizing the SEP. b) SEPs, and peptides in general, are going to be limited as therapeutics because peptides have poor stability and pharmacokinetic properties. The chemical synthesis of SEPs will enable the development of analogs with superior properties that will enable the therapeutic potential of these peptides to be realized. c) Most SEPs operate intracellularly, but most peptides cannot cross biological membranes. The addition of a cell penetrating peptide (CPP) to a SEP will enable these proteins to affect biology inside the cells.