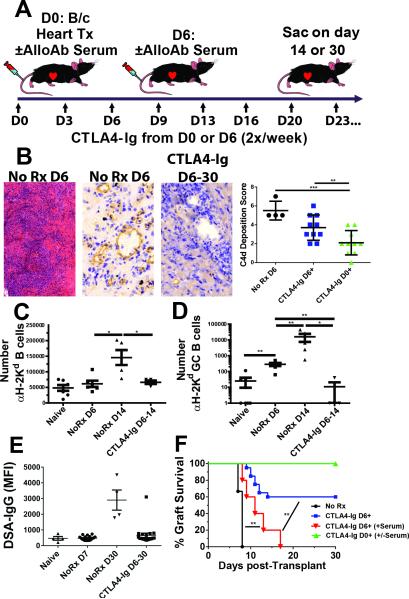
Figure 5. Delayed CTLA4-Ig rescued allogeneic heterotopic heart transplants but did not reverse established damage.
A, Diagram of experimental protocol. C57BL/6 mice were given heterotopic BALB/c hearts, and given 250μg CTLA4-Ig 2x/week starting 6d post-transplantation until sacrifice, and compared with untreated controls. Hyperimmune sera (250 uL/mouse) was injected i.v. either at D0 or D6 post-transplantation, concurrently with the initiation of CTLA4-Ig treatment. B, Histology of acutely rejecting (AR) hearts at 6d post-transplantation (Left, H&E staining, 10x magnification. Center, C4d staining, 40x magnification) or at 30d post-transplant from animals treated with CTLA4-Ig from day 6-30 post-transplant (Right, C4d staining, 40x magnification). A quantification of C4d deposition of AR hearts (NoRx D6) on day 6 post-transplant, as well as CTLA4-Ig D6+ and CTLA4-Ig D0+ on day 30 post-transplantation, is shown (far right). C, Spleens and axial, brachial, and inguinal LN cells were pooled and the total number of H-2Kd-binding B cells/per mouse were determined on day 14 post-transplantation for naïve, day 6 or 14 post-heart transplant recipients with no treatment (No Rx), or treatment with CTLA4-Ig from day 6-14 post-transplantation. D, Total number of GC B cells among H-2Kd-specific B cells with a GC phenotype. (N=4-8 per group from 4 independent experiments). E, Circulating donor-specific IgG antibodies (DSA-IgG) levels in transplanted mice at day 6-7 or ≥30 post-transplantation ± CTLA4-Ig. F, Survival of allografts in untreated and delayed CTLA4-Ig-treatment (N=6-12 per group from 5 independent experiments). Some mice received 250 uL/mouse of pooled hyperimmune serum at time of CTLA4-Ig treatment (Day0+ (N=3) or D6+ N=5 from 2 independent experiments). Statistically significant differences are indicated (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005).