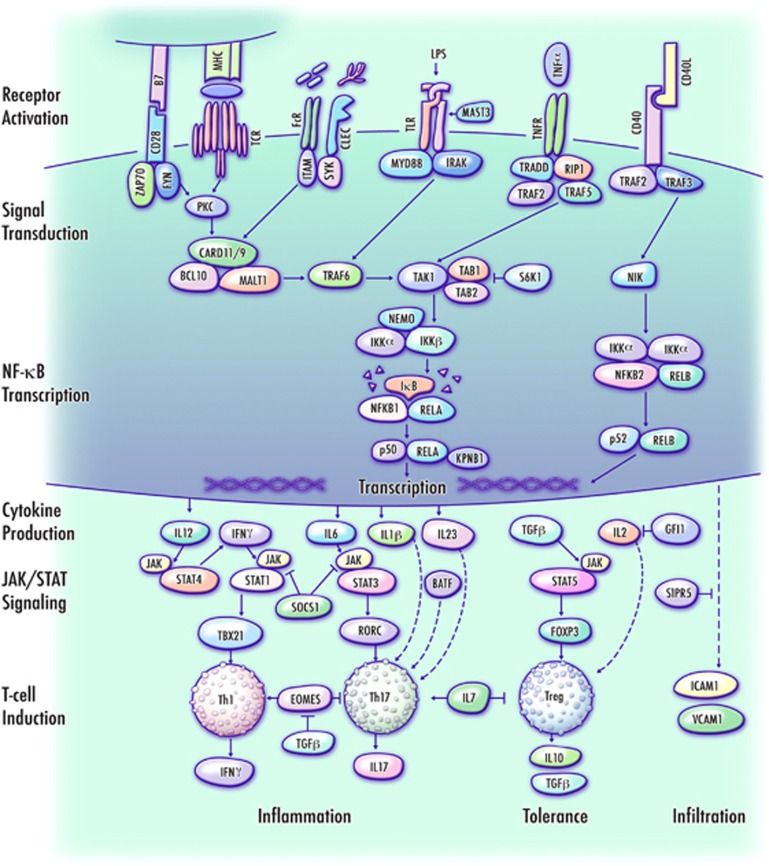
Figure 2.
NF-κB-mediated regulation of inflammatory and immunosuppressive CD4+ T-cell lineages. Proposed mechanism of MS pathology implicated by pathway analysis of GWAS-NR candidate genes. This simplified schematic presents an abridged set of interactions in an exploded format for tractability, uses generic labels for several homologous candidates (for example, B7 represents both CD80 and CD86), and does not individually depict each candidate gene implicated in current literature as having relevance to this pathway. Activation of membrane-bound T-cell receptors (TCR),75 pattern recognition receptors such as dendritic-cell Toll-like receptors and C-type lectins76, 77, 78 and receptors of the TNF superfamily79, 80 initiate signal transduction cascades leading to the activation of NF-κB transcriptional programs through canonical and non-canonical pathways, resulting in cytokine production that determines the balance between inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cells, and immunosuppressive regulatory T cells via JAK/STAT signaling to lineage-specific transcription factors.81 NF-κB activation also promotes the expression of cell adhesion molecules on vascular endothelia, which enable the infiltration of inflammatory T cells across the blood–brain barrier.62, 82 CLEC, C-type lectin; FcR, Fc receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNFR, TNF-α receptor; Th1, T helper type 1 cell; Treg, T-regulatory cell.