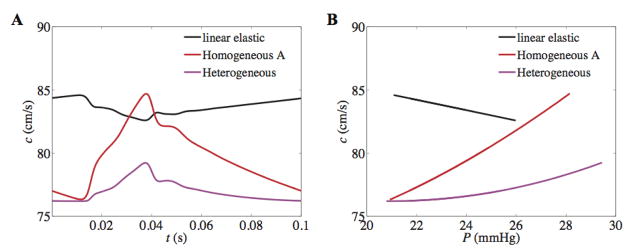
Figure 10. PWV over cardiac cycle (A) and as function of pressure (B) in the main trunk from linear and non-linear vessel mechanics.
Although the linear wall model predicts the qualitatively wrong behavior i.e. a decrease in PWV and arterial stiffness with pressure, the average PWV over the cardiac cycle is greater for the linear than the non-linear models; 83.6 ± 0.5 cm/s, 79.7 ± 2.3 cm/s and 77.0 ± 0.8 cm/s for linear-elastic, homogeneous A, and heterogeneous models, respectively.